Possible Association of Carbapenemase Production with Susceptibility Pattern and Resistance Genes Among Carbapenemase Producing Enterobacterales from Blood Isolates or Bacteremic Patients
- PMID: 40395971
- PMCID: PMC12091050
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S519561
Possible Association of Carbapenemase Production with Susceptibility Pattern and Resistance Genes Among Carbapenemase Producing Enterobacterales from Blood Isolates or Bacteremic Patients
Abstract
Background: Bacteremia caused by Enterobacteriaceae strains is associated with increased mortality rates due to antibiotic resistance, including carbapenems. The current study investigated antimicrobial susceptibility, carbapenemase production, and the presence of resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from blood cultures.
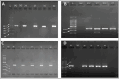
Methods: Eighty pure Enterobacteriaceae isolates were collected from positive blood cultures from four Jordanian hospitals. Antimicrobial susceptibility was investigated using the Kirby-Bauer method. Chromogenic culture media was used for the Hodge test, and the carbapenemase production was determined using the Carba NP test. The PCR technique was used to identify genes that confer resistance.
Results: Most isolates were positive for Klebsiella pneumoniae (55%), followed by Escherichia coli (37.5%) and Enterobacter cloacae (5%). The highest rates of resistance were observed against ampicillin (90%), cefazolin (76.7%), cefotaxime (70%), and ceftriaxone (65%). The lowest rate of resistance was observed against imipenem (13.7%). The frequencies of carbapenemase production, as determined by chromogenic culture media, the modified Hodge test, and the Carba NP Test, were 18.75%, 21.25%, and 10%, respectively. The identified carbapenemase resistance genes were bla-KPC (10%), bla-NDM (15%), bla-VIM (5%), and bla-OXA-48 (6.25%). A significant association (P < 0.05) was found between multidrug resistance and carbapenemase production.
Conclusion: A low percentage of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae was observed among Jordanian patients with bacteremia. A significant association was observed between carbapenemase production and multi-drug resistance. The results can be used in the management of bacteremic patients in Jordan.
Keywords: Enterobacteriaceae; Jordan; antibiotic resistance; bacteremia; carbapenemase; gene.
© 2025 Shakhatreh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

