The role of autophagy in the pathogenesis and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD)
- PMID: 40395983
- PMCID: PMC11926909
- DOI: 10.1080/27694127.2025.2474796
The role of autophagy in the pathogenesis and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD)
Abstract
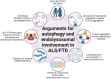
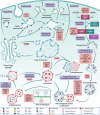
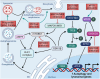
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) represent two extremes of a neurodegenerative disease spectrum characterised by overlapping genetic, clinical, and neuropathological features. This review covers the intricate relationship between both ALS and FTD and defects in the autophagy and endolysosomal pathway as recent evidence has pointed towards alterations in these pathways as being a root cause of disease pathogenesis. Here, we review the current knowledge on the interplay between ALS/FTD and lysosomebased proteostasis pathways and carefully asses the steps of the autophagy and endolysosomal pathways that are impaired by ALS or FTDcausing variants. Finally, we present a comprehensive overview of therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring autophagic and lysosomal function as potential avenues for mitigating the impact of these devastating diseases. Through this review, we aim to enhance the understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms involving autophagy and/or the endolysosomal system that underlie the ALS-FTD spectrum and underscore the necessity for specific therapeutic approaches that target these shared vulnerabilities.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); autophagosome; autophagy; endolysosome; endosome; frontotemporal dementia (FTD); lysosome; neurodegeneration.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
JB has nothing to disclose. PVD has served in advisory board meeting (paid to institution) for Biogen, CSL Behring, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Ferrer, QurAlis, Cytokinetics, Argenx, UCB, Muna Therapeutics, Alector, Augustine Therapeutics, VectorY, Sapreme Technologies, Novartis, Prilenia Therapeutics, Trace Neuroscience, NRG Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lysosome dysfunction as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases: Lessons from frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Jul;154:105360. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105360. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 33812000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The converging roles of sequestosome-1/p62 in the molecular pathways of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD).Neurobiol Dis. 2022 May;166:105653. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105653. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 35143965 Review.
-
C9orf72 ALS-FTD: recent evidence for dysregulation of the autophagy-lysosome pathway at multiple levels.Autophagy. 2021 Nov;17(11):3306-3322. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1872189. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33632058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathomechanism Heterogeneity in the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia Disease Spectrum: Providing Focus Through the Lens of Autophagy.J Mol Biol. 2020 Apr 3;432(8):2692-2713. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.02.018. Epub 2020 Feb 29. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32119873 Review.
-
The endolysosomal pathway and ALS/FTD.Trends Neurosci. 2023 Dec;46(12):1025-1041. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Trends Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37827960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycerophospholipids in ALS: insights into disease mechanisms and clinical implication.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Jul 26;20(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00876-3. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40713843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
