PIKFYVE-dependent regulation of MTORC1 and TFEB
- PMID: 40396039
- PMCID: PMC11864659
- DOI: 10.1080/27694127.2022.2082201
PIKFYVE-dependent regulation of MTORC1 and TFEB
Abstract
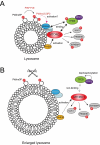
TFEB (transcription factor EB) is essential for the upregulation of gene expression required for macroautophagy/autophagy and lysosomal function. Under nutrient-rich conditions, TFEB is inactivated by MTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase) complex 1 (MTORC1)-dependent phosphorylation on the lysosome. This suppresses TFEB activity via preventing its translocation to the nucleus. Conversely, under starvation conditions and low MTORC1 activity, MTORC1 sites on TFEB are dephosphorylated, and TFEB translocates to the nucleus, where it activates its transcriptional program. We recently found that the inhibition of PIKFYVE, which produces phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate on lysosomes, leads to the dephosphorylation and translocation of TFEB to the nucleus in a manner dependent on PPP2/PP2A (protein phosphatase 2) even under nutrient-rich conditions. Importantly, interaction of TFEB with MTORC1 but not with PPP2 is disrupted when PIKFYVE is inhibited. This suggests that PIKFYVE inhibition results in a loss of contact between MTORC1 and TFEB, which allows PPP2-dependent dephosphorylation of TFEB to be dominant. Interestingly, PIKFYVE-dependent localization of MTORC1 to lysosomes and TFEB phosphorylation requires the RRAG small GTPases. Thus, PIKFYVE may play a critical role in enhancing the activity of RRAG small GTPases, and thereby act as an essential suppressor of TFEB. Therefore, in addition to its direct roles in endosome homeostasis, PIKFYVE may also exert key functions in the regulation of the TFEB-dependent transcriptional program by interacting with the lysosomal nutrient-sensing machinery.
Keywords: MTORC1; PIKFYVE; TFEB; lysosomes; phosphoinositide lipid; protein phosphatase 2A.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PP2A-dependent TFEB activation is blocked by PIKfyve-induced mTORC1 activity.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Mar 1;33(3):ar26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-06-0309. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35020443 Free PMC article.
-
TFEB-driven endocytosis coordinates MTORC1 signaling and autophagy.Autophagy. 2019 Jan;15(1):151-164. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1511504. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30145926 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomotropic drugs activate TFEB via lysosomal membrane fluidization and consequent inhibition of mTORC1 activity.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Dec 13;9(12):1191. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1227-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30546014 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of lysosomes in skeletal muscle during exercise, disuse and aging.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Nov 20;225:323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.09.028. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39332541 Review.
-
Therapeutic regulation of autophagy in hepatic metabolism.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.021. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic and Mechanistic Insights Inform Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment and Symptomatic Management: Current and Emerging Therapeutics and Clinical Trial Design Considerations.CNS Drugs. 2025 Oct;39(10):949-993. doi: 10.1007/s40263-025-01217-0. Epub 2025 Sep 2. CNS Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40897992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
