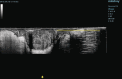
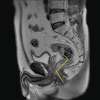
Evaluating Extended Field of View Imaging for Measuring Rectal Tumor Lowest Boundary to Anal Verge Distance via Transrectal Biplane Ultrasound
- PMID: 40396169
- PMCID: PMC12090980
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2569-6939
Evaluating Extended Field of View Imaging for Measuring Rectal Tumor Lowest Boundary to Anal Verge Distance via Transrectal Biplane Ultrasound
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to measure the precise distance from the lowest boundary of a rectal tumor to the anal verge (DTAV) in patients with rectal cancer.
Materials and methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on clinical data from 70 rectal cancer patients. DTAV measurements were collected using transrectal biplane ultrasound, MRI, and colonoscopy.
Results: The difference in DTAV measurements between the mean DTAV value obtained by ultrasound (US mean ) and colonoscopy exhibited a difference of 0.22 cm. In contrast, the difference between US mean and MRI was 0.48 cm, while the difference between MRI and colonoscopy was -0.26 cm. The ICC for DTAV measurements demonstrated excellent agreement, with values of 0.948 between US mean and MRI, 0.942 between US mean and colonoscopy, and 0.943 between MRI and colonoscopy. The minimum DTAV value obtained by ultrasound (US min ) was 5.05 cm, the middle DTAV value obtained by ultrasound (US mid ) was 5.10 cm, and the maximum DTAV value obtained by ultrasound (US max ) was 5.30 cm. Notably, the median values of the differences in DTAV measurements between US max and US min , US max and US mid , as well as US mid and US min , were 0.2 cm, 0.1 cm, and 0.1 cm, respectively. Furthermore, the consistency of DTAV measurements between US min and US mid , US max and US mid , as well as US min and US max was excellent, with all ICC values reaching 0.999. Additionally, the radiologist's reassessment of MRI DTAV data showed excellent consistency with the original results, with an ICC value of 0.985.
Conclusion: Transrectal biplane ultrasound utilizing EFOV imaging technology exhibited both accuracy and reproducibility for measuring DTAV. This approach provided a highly efficient and practical clinical tool for DTAV measurement.
Keywords: MR imaging; colonoscopy; extended field of view technology; rectal cancer; transrectal biplane ultrasound.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A boundary-guided transformer for measuring distance from rectal tumor to anal verge on magnetic resonance images.Patterns (N Y). 2023 Mar 27;4(4):100711. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2023.100711. eCollection 2023 Apr 14. Patterns (N Y). 2023. PMID: 37123445 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring distance from lowest boundary of rectal tumor to anal verge on CT images using pyramid attention pooling transformer.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Mar;155:106675. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106675. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36805228
-
Sagittal FOCUS-MUSE Diffusion-weighted Imaging MRI Improves the Accuracy of Rectal Cancer Location: A Prospective Observational Study.Acad Radiol. 2025 Jun 9:S1076-6332(25)00527-6. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2025.05.050. Online ahead of print. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40494696
-
Distance to the anal verge is associated with pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2016 Oct;114(5):637-641. doi: 10.1002/jso.24358. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27641934 Free PMC article.
-
Value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in deep angiomyxoma using a biplane transrectal probe: A case report.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jul 14;29(26):4214-4221. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i26.4214. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37475848 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

