Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characteristics of bovine mastitis-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: potential for cross-species transmission of ST59-MRSA
- PMID: 40396723
- PMCID: PMC12210863
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02800-24
Antimicrobial resistance and molecular characteristics of bovine mastitis-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: potential for cross-species transmission of ST59-MRSA
Abstract
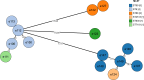
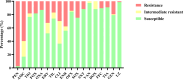
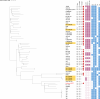
Mastitis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a common issue in dairy farming, with sequence types (STs) related to cows mainly including ST9 and ST97. ST59, the predominant community-acquired clone, is still less reported in dairy cows. This study investigated the antimicrobial resistance patterns and molecular characteristics of 77 Staphylococcus aureus isolates obtained from eight dairy farms in the mid-east of China during 2019-2020, focusing particularly on the bovine mastitis-related livestock-associated MRSA (LA-MRSA) clone ST59. Among the 77 isolates, 14 isolates were identified as MRSA. A total of 20 STs were identified, with ST59 being the most prevalent among MRSA isolates (35.7%). All MRSA isolates possessed various Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) types, including XII (n = 5), IV.a (n = 4), IV.c (n = 2), IV.g (n = 2), and V (n = 1). Three MRSA lineages were identified: MRSA-ST59-t437-SCCmec IV.a/IV.g (n = 5), MRSA-ST9-t899-SCCmec XII (n = 4), and MRSA-ST88-t3622-SCCmec IV.c (n = 2). Approximately 44.2% of isolates demonstrated multidrug resistance. MRSA isolates showed a higher prevalence of antimicrobial resistance compared to methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) isolates. Virulence factor assays revealed that all MRSA isolates carried at least hemolysin genes and enterotoxin genes. ST59-MRSA strains showed the closest genetic relationship with human-derived strains, indicating a potential public health risk due to transmission of Staphylococcus aureus between livestock and humans. This study highlights the significant prevalence of the bovine mastitis-related LA-MRSA clone ST59 in the mid-east of China. Therefore, reinforcing monitoring and implementing preventive measures are essential to combat LA-MRSA.
Importance: Obtained the prevalence and molecular characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus in dairy farms in the mid-east of China from 2019 to 2020. Recently identified livestock-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus (LA-MRSA) clones in cattle, including ST59-MRSA, may have originated from human sources, suggesting a potential risk for interspecies transmission.
Keywords: ST59; bovine mastitis; livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus; molecular characteristics; multidrug-resistant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Liu H, Ji X, Wang H, Hou X, Sun H, Billington C, Zhang L, Wang X, Wang R. 2023. Genomic epidemiology and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk in Jiangsu, China: emerging broader host tropism strain clones ST59 and ST398. Front Microbiol 14:1266715. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1266715 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

