Invasive lobular breast carcinoma variants; clinicopathological features and patient outcomes
- PMID: 40397321
- PMCID: PMC12133914
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-025-07729-z
Invasive lobular breast carcinoma variants; clinicopathological features and patient outcomes
Abstract
Introduction: An understanding of the differences among the invasive lobular breast carcinoma (ILC) variants is crucial for risk stratification, and tailored treatment planning. This article compares variants of ILC according to their clinical outcomes and histopathological features.
Patients and methods: Patients diagnosed with ILC between January 2010 and August 2021 were retrospectively evaluated. Patients were divided into three groups; 1: classic ILC (cILC); 2: pleomorphic lobular carcinoma (PLC); 3: mixed ILC. Mixed ILC was divided into three subgroups: 3a, cILC + PLC; 3b, cILC + mixed; 3c, PLC + mixed.
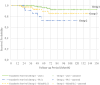
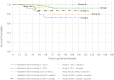
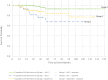
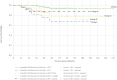
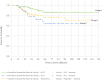
Results: A total of 254 patients were included in the study. Median overall survival (OS) was 48 months, and median disease-free survival (DFS) was 46 months. Locoregional recurrence (LRR) occurred in 15 (5.9%) of the patients, and distant metastasis (DM) developed in 23 (9.1%). Death occurred in 16 (6.3%) patients. There was no significant difference in LRR rate among groups. When considering five groups (Groups 1, 2, 3a, 3b, and 3c), the median OS was 62.5, 52.0, 50.8, 56.7, and 41.5 months, respectively, while the median DFS was 60.3, 46.6, 46.7, 54.5, and 39.6 months, respectively. Notably, the PLC + mixed group without a classic variant (Group 3c) exhibited even worse outcomes than pure PLC.
Conclusions: In this study, pure cILC exhibited the best prognostic features among the ILC variants. Furthermore, we observed a higher mastectomy rate in patients with pleomorphic variants. Surgical management of ILC remains controversial. Moreover, comprehensive randomized controlled trials are essential to establish standardized treatment protocols for ILC patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Classic variant; Invasive lobular breast carcinoma; Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma; Surgery; Survival.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Van Baelen K, Nguyen HL, Hamy-Petit AS, Richard F, Karsten MM, Nader Marta G, Vermeulen P, Toussaint A, Reyal F, Vincent-Salomon A, Dirix L, Dordevic AD, de Azambuja E, Larsimont D, Amato O, Maetens M, De Schepper M, Geukens T, Han SN, Baert T, Punie K, Wildiers H, Smeets A, Nevelsteen I, Floris G, Biganzoli E, Neven P, Desmedt C (2023) Association of body mass index with clinicopathological features and survival in patients with primary invasive lobular breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 191:112988. 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.112988 - PubMed
-
- Van Baelen K, Geukens T, Maetens M, Tjan-Heijnen V, Lord CJ, Linn S, Bidard FC, Richard F, Yang WW, Steele RE, Pettitt SJ, Van Ongeval C, De Schepper M, Isnaldi E, Nevelsteen I, Smeets A, Punie K, Voorwerk L, Wildiers H, Floris G, Vincent-Salomon A, Derksen PWB, Neven P, Senkus E, Sawyer E, Kok M, Desmedt C (2022) Current and future diagnostic and treatment strategies for patients with invasive lobular breast cancer. Ann Oncol 33(8):769–785. 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.05.006 - PubMed
-
- Sledge GW, Chagpar A, Perou C (2016) Collective wisdom: lobular carcinoma of the breast. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 35:18–21. 10.1200/EDBK_100002 - PubMed
-
- Biglia N, Mariani L, Sgro L, Mininanni P, Moggio G, Sismondi P (2007) Increased incidence of lobular breast cancer in women treated with hormone replacement therapy: implications for diagnosis, surgical and medical treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer 14(3):549–567. 10.1677/ERC-06-0060 - PubMed
-
- Christgen M, Steinemann D, Kühnle E, Länger F, Gluz O, Harbeck N, Kreipe H (2016) Lobular breast cancer: clinical, molecular and morphological characteristics. Pathol Res Pract 212(7):583–597. 10.1016/j.prp.2016.05.002 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

