Bioengineered Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vehicles Suppressed Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis and Bevacizumab Resistance
- PMID: 40397411
- PMCID: PMC12199312
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202417714
Bioengineered Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vehicles Suppressed Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis and Bevacizumab Resistance
Abstract
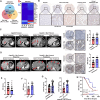
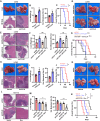
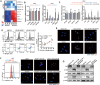
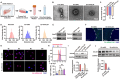
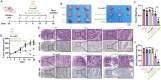
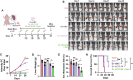
Antiangiogenic therapies, such as bevacizumab, are among the causes of cancer-related death in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) with liver metastasis. Delivering siRNAs via primary cell originating from primary cells is a promising method for targeting CRC liver metastasis and drug resistance. Here, it is found that the expression of CCL24 is significantly upregulated in tumor tissues at the CRC liver metastasis site. In addition, CCL24 is significantly upregulated in tumor tissues from bevacizumab-resistant patients. CCL24 promotes the formation of inflammatory tumor-associated fibroblast subsets in the CRC liver metastasis microenvironment and induces resistance to bevacizumab therapy. Based on these results, a primary cell-derived extracellular vehicle delivery system is designed for the simultaneous delivery of siRNAs targeting CCL24 in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Downregulation of CCL24 in the TME by delivering bioengineered extracellular vehicles significantly increased sensitivity to antiangiogenic therapy in a CRC mouse model. A novel therapeutic target is identified for patients with CRC with liver metastasis and suggested a possible therapeutic alternative for patients with CRC with resistance to antiangiogenic therapy and distant metastasis.
Keywords: antiangiogenic therapy; colorectal cancer; engineered extracellular vehicles; liver metastasis; siRNA delivery.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic review and economic evaluation of bevacizumab and cetuximab for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Mar;11(12):1-128, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta11120. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17346499
-
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for diabetic macular oedema: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD007419. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007419.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 16;10:CD007419. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007419.pub6. PMID: 28639415 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Colorectal Cancer Cells-Derived Exosomal PIK3CA Mutation DNA Promotes Tumor Metastasis by Activating Fibroblast and Affecting Tumor Metastatic Microenvironment.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jul;12(27):e2501792. doi: 10.1002/advs.202501792. Epub 2025 May 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40344411 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular-endothelial-growth-factor (VEGF) targeting therapies for endocrine refractory or resistant metastatic breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jul 11;2012(7):CD008941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008941.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22786517 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenesis inhibitors for the treatment of ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Sep 7;(9):CD007930. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007930.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Apr 18;4:CD007930. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007930.pub3. PMID: 21901715 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- a) Giuliante F., Vigano L., De Rose A. M., Mirza D. F., Lapointe R., Kaiser G., Barroso E., Ferrero A., Isoniemi H., Lopez‐Ben S., Popescu I., Ouellet J. F., Hubert C., Regimbeau J. M., Lin J. K., Skipenko O. G., Ardito F., Adam R., Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 8198; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Leone N., Arolfo S., Spadi R., Fortunato M. R., Passera R., Morino M., Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2023, 38, 169; - PubMed
- c) Shepherdson M., Kilburn D., Ullah S., Price T., Karapetis C. S., Nguyen P., Townsend A., Padbury R., Piantadosi C., Maddern G., Carruthers S., Roder D., Sorich M., Roy A. C., ANZ J. Surg. 2023, 93, 1847. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
