Nonenzymatic RNA copying with a potentially primordial genetic alphabet
- PMID: 40397670
- PMCID: PMC12130883
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2505720122
Nonenzymatic RNA copying with a potentially primordial genetic alphabet
Abstract
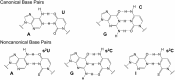
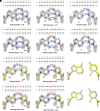
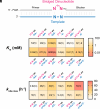
Nonenzymatic RNA copying is thought to have been responsible for the replication of genetic information during the origin of life. However, chemical copying with the canonical nucleotides (A, U, G, and C) strongly favors the incorporation of G and C and disfavors the incorporation of A and especially U because of the stronger G:C vs. A:U base pair and the weaker stacking interactions of U. Recent advances in prebiotic chemistry suggest that the 2-thiopyrimidines were precursors to the canonical pyrimidines, raising the possibility that they may have played an important early role in RNA copying chemistry. Furthermore, 2-thiouridine (s2U) and inosine (I) form by deamination of 2-thiocytidine (s2C) and A, respectively. We used thermodynamic and crystallographic analyses to compare the I:s2C and A:s2U base pairs. We find that the I:s2C base pair is isomorphic and isoenergetic with the A:s2U base pair. The I:s2C base pair is weaker than a canonical G:C base pair, while the A:s2U base pair is stronger than the canonical A:U base pair, so that a genetic alphabet consisting of s2U, s2C, I, and A generates RNA duplexes with uniform base pairing energies. Consistent with these results, kinetic analysis of nonenzymatic template-directed primer extension reactions reveals that s2C and s2U substrates bind similarly to I and A in the template, and vice versa. Our work supports the plausibility of a potentially primordial genetic alphabet consisting of s2U, s2C, I, and A and offers a potential solution to the long-standing problem of biased nucleotide incorporation during nonenzymatic template copying.
Keywords: 2-thiocytidine; inosine; noncanonical base pair; nonenzymatic RNA replication; origin of life.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unusual Base Pair between Two 2-Thiouridines and Its Implication for Nonenzymatic RNA Copying.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Feb 14;146(6):3861-3871. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c11158. Epub 2024 Jan 31. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38293747 Free PMC article.
-
Replacing uridine with 2-thiouridine enhances the rate and fidelity of nonenzymatic RNA primer extension.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Feb 25;137(7):2769-75. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00445. Epub 2015 Feb 16. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25654265 Free PMC article.
-
Diaminopurine in Nonenzymatic RNA Template Copying.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Jun 12;146(23):15897-15907. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c02560. Epub 2024 May 31. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38818863 Free PMC article.
-
The Emergence of RNA from the Heterogeneous Products of Prebiotic Nucleotide Synthesis.J Am Chem Soc. 2021 Mar 10;143(9):3267-3279. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c12955. Epub 2021 Feb 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2021. PMID: 33636080 Review.
-
The G x U wobble base pair. A fundamental building block of RNA structure crucial to RNA function in diverse biological systems.EMBO Rep. 2000 Jul;1(1):18-23. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd001. EMBO Rep. 2000. PMID: 11256617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Szostak J. W., The eightfold path to non-enzymatic RNA replication. J. Syst. Chem. 3, 1–14 (2012).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

