Macrophage hitchhiking nanomedicine for enhanced β-elemene delivery and tumor therapy
- PMID: 40397726
- PMCID: PMC12094207
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adw7191
Macrophage hitchhiking nanomedicine for enhanced β-elemene delivery and tumor therapy
Abstract
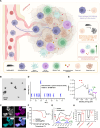
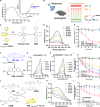
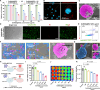
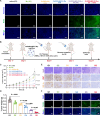
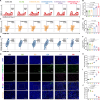
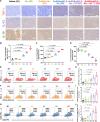
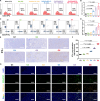
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems hold promise for tumor therapy; however, they frequently encounter challenges such as low delivery efficiency and suboptimal efficacy. Engineered living cells can redirect drug delivery systems to effectively reach targeted sites. Here, we used living macrophages as vehicles, attaching them with GeS nanosheets (GeSNSs) carrying β-elemene for transport to tumor sites. GeSNSs act as efficient sonosensitizers, enhancing ultrasound-induced reactive oxygen species generation for treating 4T1 breast tumors. Notably, macrophage hitchhiking delivery of β-elemene-loaded GeSNSs not only achieves high accumulation in tumor regions and suppresses tumor growth under ultrasound treatment, but also effectively remodels the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by improving M1-like macrophage polarization and enhancing the populations of mature dendritic cells, CD4+, and CD8+ lymphocytes, thereby facilitating enhanced sonodynamic chemoimmunotherapy. These findings underscore the potential of macrophage hitchhiking strategy for drug delivery and suggest broader applicability of engineered living materials-mediated delivery technologies in disease therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Brody H., Innovative cancer therapies offer new hope. Nature 629, S1 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Chen W., Li Y., Liu C., Kang Y., Qin D., Chen S., Zhou J., Liu H. J., Ferdows B. E., Patel D. N., Huang X., Koo S., Kong N., Ji X., Cao Y., Tao W., Xie T., In situ engineering of tumor-associated macrophages via a nanodrug-delivering-drug (β-Elemene@Stanene) strategy for enhanced cancer chemo-immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202308413 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

