Astrocyte-derived CCL5-mediated CCR5+ neutrophil infiltration drives depression pathogenesis
- PMID: 40397747
- PMCID: PMC12094238
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt6632
Astrocyte-derived CCL5-mediated CCR5+ neutrophil infiltration drives depression pathogenesis
Abstract
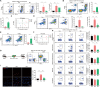
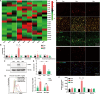
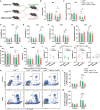
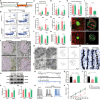
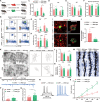
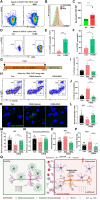
Cross-talk between the nervous and immune systems is involved in neurological diseases. However, their potential interplay in depression has yet to be elucidated. Here, using single-cell RNA and neutrophil SMART RNA sequencing, we showed that CCR5+ neutrophils were significantly increased in patients with depression and preferentially migrated to the hippocampus in a mouse model of depression. Infiltrated neutrophils engulf neuronal spines and subsequently promote depressive symptoms in male mice. Furthermore, by genetic or pharmacologic disruption, we identified a chemotactic effect of the astrocyte-derived chemokine CCL5 on mediating the infiltration of CCR5+ neutrophils and behavioral disorders in male depressed mice. Our findings therefore highlight the critical role of neutrophils in depression pathogenesis and astrocytes in mediating the dysregulation of innate immune responses and suggest that inhibition of CCL5/CCR5-mediated neutrophil infiltration represents a potential therapeutic strategy for noninfectious brain diseases such as depression.
Figures



References
-
- Fan Z., Chang J., Liang Y., Zhu H., Zhang C., Zheng D., Wang J., Xu Y., Li Q. J., Hu H., Neural mechanism underlying depressive-like state associated with social status loss. Cell 186, 560–576.e17 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Marwaha S., Palmer E., Suppes T., Cons E., Young A. H., Upthegrove R., Novel and emerging treatments for major depression. Lancet 401, 141–153 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

