Effects of mini-dose esketamine-dexmedetomidine combination supplemented intravenous analgesia on postoperative sleep quality in elderly patients after total knee arthroplasty: a protocol of double-blind randomised trial
- PMID: 40398940
- PMCID: PMC12096973
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-098018
Effects of mini-dose esketamine-dexmedetomidine combination supplemented intravenous analgesia on postoperative sleep quality in elderly patients after total knee arthroplasty: a protocol of double-blind randomised trial
Abstract
Introduction: Postoperative sleep quality is generally impaired in elderly patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Decreased postoperative sleep quality seriously affects postoperative recovery. Both esketamine and dexmedetomidine have been individually demonstrated to have the potential to enhance postoperative sleep quality. However, the effectiveness of mini-dose esketamine-dexmedetomidine supplemented intravenous analgesia on postoperative sleep quality remains to be elucidated.
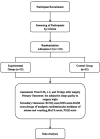
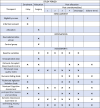
Methods and analysis: 110 elderly patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty will be randomly assigned to different regimens of patient-controlled intravenous analgesia with a total volume of 100 mL in either the experimental group (sufentanil 1.5 µg/kg+esketamine 25 mg+dexmedetomidine 100 µg) or the control group (sufentanil 1.5 µg/kg+equal vol of placebo, ie, saline). The primary outcome is the subjective sleep quality score on the night of surgery, assessed using the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire. The secondary outcomes are the Richards-Campbell Sleep Questionnaire scores on the first and second postoperative nights. Patients' pain scores, Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale scores, analgesic medication usage and incidence of nausea and vomiting are documented two times per day for two postoperative days. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment score is assessed on the day of discharge. Regarding other outcomes, telephone follow-up will be performed at 30 days postoperatively to assess the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index score and identify and document major complications within 30 days. Safety outcomes encompass not only the monitoring of basic vital signs such as hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, bradycardia and low peripheral oxygen saturation but also psychiatric symptoms, including nightmares, hallucinations, restlessness, confusion, diplopia and blurred vision. The analysis will be conducted according to the principle of intention-to-treat.
Ethics and dissemination: The study protocol has been approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee of Weifang People's Hospital (KYLL20240523-1). The results of the study will be published in peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2400085253.
Keywords: ANAESTHETICS; Anaesthesia in orthopaedics; Pain management; Sleep medicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
