Deciphering the history of ERK activity from fixed-cell immunofluorescence measurements
- PMID: 40399273
- PMCID: PMC12095524
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58348-7
Deciphering the history of ERK activity from fixed-cell immunofluorescence measurements
Abstract
The RAS/ERK pathway plays a central role in diagnosis and therapy for many cancers. ERK activity is highly dynamic within individual cells and drives cell proliferation, metabolism, and other processes through effector proteins including c-Myc, c-Fos, Fra-1, and Egr-1. These proteins are sensitive to the dynamics of ERK activity, but it is not clear to what extent the pattern of ERK activity in an individual cell determines effector protein expression, or how much information about ERK dynamics is embedded in the pattern of effector expression. Here, we evaluate these relationships using live-cell biosensor measurements of ERK activity, multiplexed with immunofluorescence staining for downstream target proteins of the pathway. Combining these datasets with linear regression, machine learning, and differential equation models, we develop an interpretive framework for immunofluorescence data, wherein Fra-1 and pRb levels imply long-term activation of ERK signaling, while Egr-1 and c-Myc indicate more recent activation. Analysis of multiple cancer cell lines reveals a distorted relationship between ERK activity and cell state in malignant cells. We show that this framework can infer various classes of ERK dynamics from effector protein stains within a heterogeneous population, providing a basis for annotating ERK dynamics within fixed cells.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: John Albeck has received research grants from Kirin Corporation. The other authors declare no competing interests. Inclusion and Ethics: All collaborators have fulfilled the criteria for authorship required by Nature Portfolio and are included as authors of this study. This research is locally relevant and included local researchers throughout the entire research process including study design, study implementation, data ownership, intellectual property, and authorship of publications. Roles and responsibilities were agreed amongst collaborators ahead of the research. This research was not severely restricted or prohibited in the researchers’ setting. This work does not result in stigmatization, incrimination, discrimination or otherwise personal risk to participants, nor does it risk the health, safety, and security of the researchers. We have considered relevant local and regional research in the citations.
Figures
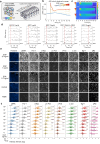

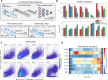
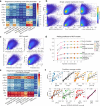
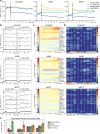

Update of
-
Deciphering the History of ERK Activity from Fixed-Cell Immunofluorescence Measurements.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 17:2024.02.16.580760. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.16.580760. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 21;16(1):4721. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58348-7. PMID: 38405841 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Lavoie, H., Gagnon, J. & Therrien, M. ERK signalling: a master regulator of cell behaviour, life and fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.21, 607–632 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Jones, S. M. & Kazlauskas, A. Growth-factor-dependent mitogenesis requires two distinct phases of signalling. Nat. Cell Biol.3, 165–172 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R25 GM056765/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007377/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35GM139621/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01HL151983/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- U54CA283766/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- T32 GM007377/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151983/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R25GM056765/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- U54 CA283766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM115650/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM115650/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35 GM139621/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

