Stepwise ATP translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum by human SLC35B1
- PMID: 40399679
- PMCID: PMC12267056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09069-w
Stepwise ATP translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum by human SLC35B1
Abstract
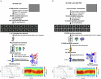
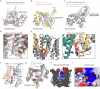
ATP generated in the mitochondria is exported by an ADP/ATP carrier of the SLC25 family1. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) cannot synthesize ATP but must import cytoplasmic ATP to energize protein folding, quality control and trafficking2,3. It was recently proposed that a member of the nucleotide sugar transporter family, termed SLC35B1 (also known as AXER), is not a nucleotide sugar transporter but a long-sought-after ER importer of ATP4. Here we report that human SLC35B1 does not bind nucleotide sugars but indeed executes strict ATP/ADP exchange with uptake kinetics consistent with the import of ATP into crude ER microsomes. A CRISPR-Cas9 cell-line knockout demonstrated that SLC35B1 clusters with the most essential SLC transporters for cell growth, consistent with its proposed physiological function. We have further determined seven cryogenic electron microscopy structures of human SLC35B1 in complex with an Fv fragment and either bound to an ATP analogue or ADP in all major conformations of the transport cycle. We observed that nucleotides were vertically repositioned up to approximately 6.5 Å during translocation while retaining key interactions with a flexible substrate-binding site. We conclude that SLC35B1 operates by a stepwise ATP translocation mechanism, which is a previously undescribed model for substrate translocation by an SLC transporter.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: G.S.-F. is co-founder and owns shares of Solgate GmbH, an SLC-focused company. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Hirschberg, C. B., Robbins, P. W. & Abeijon, C. Transporters of nucleotide sugars, ATP, and nucleotide sulfate in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Annu. Rev. Biochem.67, 49–69 (1998). - PubMed

