iCliff Taylor's Version: Robust and Efficient Activity Cliff Determination
- PMID: 40400300
- PMCID: PMC12151610
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00506
iCliff Taylor's Version: Robust and Efficient Activity Cliff Determination
Abstract
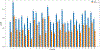
Activity cliffs represent an important challenge to tackle in cheminformatics and drug design. One of the most common indicators to quantify them is the Structure-Activity Landscape Index (SALI). Here, we expose the mathematical limitations of SALI's formulation, the most evident: it is undefined in instances where the similarity between two molecules is one. We show how using a simple Taylor's series can aid this main problem, yielding a defined expression that can capture the ranking information from the original SALI. The second issue to solve is the quadratic complexity of using SALI to describe the roughness of the activity landscape of a set. Here, we propose iCliff, an indicator that can quantify the roughness in linear complexity. For this, we leverage the iSIM framework to obtain the average similarity of the set and a rearrangement to obtain the average of the squared property differences. The calculations for 30 different AC-focused databases suggest that there is a strong correlation between iCliff and the average pairwise of SALI's pairwise Taylor Series. To further explore the individual effects of removing each molecule in the activity landscape, we propose complementary iCliff. With this tool, we were able to identify the molecules that have a high number of activity cliffs with the rest of the molecules in the set.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Update of
-
iCliff Taylor's version: Robust and Efficient Activity Cliff Determination.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 13:2025.03.09.642269. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.09.642269. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 9;65(11):5801-5810. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00506. PMID: 40161667 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
iCliff Taylor's version: Robust and Efficient Activity Cliff Determination.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 13:2025.03.09.642269. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.09.642269. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Jun 9;65(11):5801-5810. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5c00506. PMID: 40161667 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Exploring uncharted territories: predicting activity cliffs in structure-activity landscapes.J Chem Inf Model. 2012 Aug 27;52(8):2181-91. doi: 10.1021/ci300047k. Epub 2012 Aug 16. J Chem Inf Model. 2012. PMID: 22873578 Free PMC article.
-
iSIM: instant similarity.Digit Discov. 2024 May 7;3(6):1160-1171. doi: 10.1039/d4dd00041b. eCollection 2024 Jun 12. Digit Discov. 2024. PMID: 38873032 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of effective atomic number calculations for dual-energy CT.Med Phys. 2021 Oct;48(10):5908-5923. doi: 10.1002/mp.15166. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34390593 Review.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Undersampling techniques for non-linear chemical space visualization.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 7:2025.07.03.663077. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.03.663077. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40672189 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Silipo C; Vittoria A QSAR, Rational Approaches to the Design of Bioactive Compounds. In European Symposium on Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships 1990: Sorrento, Italy); 1991.
-
- Johnson MA; Maggiora GM Concepts and Applications of Molecular Similarity, 1st ed.; Wiley-Interscience, 1990.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

