Inhibition of tau aggregation by the CCT3 and CCT7 apical domains
- PMID: 40400346
- PMCID: PMC12095920
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.70162
Inhibition of tau aggregation by the CCT3 and CCT7 apical domains
Abstract
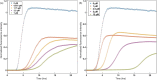
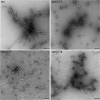
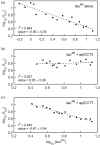
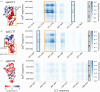
The eukaryotic chaperonin containing t-complex polypeptide 1 (CCT/TRiC) is a molecular chaperone that assists protein folding in an ATP-driven manner. It consists of two stacked identical rings that are each made up of eight distinct subunits. Here, we show that the apical domains of subunits CCT3 and CCT7 from humans are strong inhibitors of tau aggregation, which is associated with several neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Kinetic analyses and negative-stain electron microscopy indicate that the mechanism of inhibition of tau aggregation by the apical domains of subunits CCT3 and CCT7 differ. Aggregation of tau alone, or in the presence of the apical domain of subunit CCT7, can be described by a fragmentation model whereas in the presence of the apical domain of subunit CCT3, it fits a saturating elongation and fragmentation mechanism. Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations show that tau interacts with different regions in the apical domains of subunits CCT3 and CCT7, in agreement with their different inhibition mechanisms.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CCT/TRiC; chaperonins; protein aggregation; tau.
© 2025 The Author(s). Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures
References
-
- Azia A, Levy Y. Nonnative electrostatic interactions can modulate protein folding: molecular dynamics with a grain of salt. J Mol Biol. 2009;393:527–542. - PubMed
-
- Balchin D, Hayer‐Hartl M, Hartl FU. In vivo aspects of protein folding and quality control. Science. 2016;353:aac4354. - PubMed
-
- Barghorn S, Davies P, Mandelkow E. Tau paired helical filaments from Alzheimer's disease brain and assembled in vitro are based on β‐structure in the core domain. Biochemistry. 2004;43:1694–1703. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

