Genetics of catatonia: a systematic review of case reports and a gene pathway analysis
- PMID: 40400398
- PMCID: PMC12188362
- DOI: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2025.2458
Genetics of catatonia: a systematic review of case reports and a gene pathway analysis
Abstract
Background: Neurodevelopmental conditions are crucial risk factors for catatonia in pediatric and adult populations. Recent case reports and studies have identified an increasing number of genetic abnormalities likely contributing to catatonia. Catatonia associated with genetic abnormalities is challenging in terms of identification, chronicity, and resistance to treatment. In addition, understanding these genetic abnormalities through identifying rare single nucleotide and copy number variants may offer valuable insights into the underlying pathophysiology.
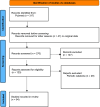
Methods: We conducted a systematic review of all genetic abnormalities reported with catatonia and performed a gene-set enrichment analysis. Our systematic literature search for relevant articles published through July 15, 2024, using combinations of "catatonia," "catatonic syndrome," "genetic," and "genes" in PubMed, yielded 317 articles. Of these, 94 were included, covering 374 cases of catatonia and 78 distinct genetic abnormalities.
Results: This review discusses the clinical presentation of catatonia for each genetic disorder, the treatment strategies, and the putative underlying mechanisms.
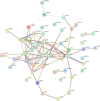
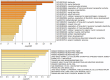
Conclusions: The review highlights that catatonia underpinned by genetic abnormalities presents specific clinical and treatment-response features. Therefore, we propose genetic testing guidelines for catatonia and advocate for systematically investigating catatonia in several genetic diseases. Regarding the pathophysiology of catatonia, the gene ontology of biological processes reveals significant enrichment of variants in synaptic and post-synaptic regulatory genes, particularly within GABAergic neurons, reinforcing the implication of the excitatory/inhibitory imbalance. Finally, genetic variants are enriched in microglial cells, highlighting the role of brain inflammation in triggering catatonia. This comprehensive insight could pave the way for more effective management strategies for this condition.
Keywords: GABAergic interneurons; catatonic syndrome; excitation/inhibition imbalance; genetic; neurodevelopmental; variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there are no conflicts of interest concerning the subject of this study.
Figures

References
-
- Walther S, Nadesalingam N, Nuoffer M, Kyrou A, Wüthrich F, Lefebvre S. Structural alterations of the motor cortex and higher order cortical areas suggest early neurodevelopmental origin of catatonia in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2022:S0920996422003747. 10.1016/j.schres.2022.10.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

