Clonal plasma cell features in light chain amyloidosis are associated with depth and timing of cardiac response independent of hematologic response
- PMID: 40400470
- PMCID: PMC12580697
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2025.287848
Clonal plasma cell features in light chain amyloidosis are associated with depth and timing of cardiac response independent of hematologic response
Abstract
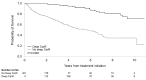
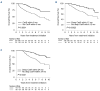
Cardiac response is associated with survival in AL amyloidosis, but substantial variation exists in response kinetics. We investigated variables associated with deep cardiac responses to characterize the factors that govern organ recovery. We retrospectively studied newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis patients (N=401) diagnosed between 2010-2022 in whom cardiac response could be assessed. Cardiac responses were recorded at 6, 12 and 24 months and the best cardiac response. A deep cardiac response was defined as a cardiac very good partial response or better (>60% reduction in baseline N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide or ≤350 pg/mL). High-risk cytogenetic abnormalities (HRCA) included del(17p), t (4;14), t(14;16), and t(14;20). Logistic and competing-risk regression analyses (treating death as a competing event) were used to examine variables associated with cardiac response. The median age of the patients was 65 years, and their median follow- up was 5.5 years. At the 6-, 12- and 24-month and best overall response landmarks, 12%, 24%, 33% and 45%, respectively, of patients had obtained a cardiac very good partial response or better. Having baseline bone marrow plasma cells (BMPC) ≥20%, obtaining a hematologic very good partial response or better within 6 months, having a κ isotype, having HRCA and undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) were significantly associated with deep cardiac response on logistic regression and competing-risk analysis. In line with their impact on cardiac response, ASCT, κ isotype and deep hematologic response within 6 months were associated with improved overall survival on multivariable Cox proportional hazards modeling. Conversely, high BMPC burden and the presence of HRCA had no association with overall survival on adjusted analysis. As this cohort was retrospectively selected for cardiac response assessment, these results need to be interpreted accordingly. Nonetheless, the association between a 'myeloma phenotype' and cardiac response kinetics, endorses the role of direct light chain toxicity and suggests that clonal plasma cell features significantly influence organ response in AL amyloidosis.
Figures

References
-
- Muchtar E, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, et al. Treatment of AL amyloidosis: Mayo Stratification of Myeloma and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) consensus statement 2020 update. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(6):1546-1577. - PubMed
-
- Palladini G, Milani P, Merlini G. Management of AL amyloidosis in 2020. Blood. 2020;136(23):2620-2627. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

