Examining the role of psychological flexibility and unconditional self-acceptance as mediators in the relationship between new media literacy and psychological wellbeing among Gen Z
- PMID: 40400595
- PMCID: PMC12094439
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1077_24
Examining the role of psychological flexibility and unconditional self-acceptance as mediators in the relationship between new media literacy and psychological wellbeing among Gen Z
Abstract
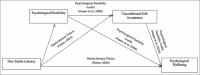
Background: This study explores the relationship between new media literacy (NML), psychological flexibility (PF), and unconditional self-acceptance (USA) in shaping the psychological wellbeing (PWB) of Generation Z.
Materials and methods: With a focus on university students aged 18 to 25, this research employed a purposive sampling method to gather data from 233 participants through online surveys. The online survey consists of four sections: New media literacy scale, Acceptance and action questionnaire (AAQ-II), The Psychological Wellbeing Scale (PWBS), and Unconditional Self-Acceptance Questionnaire (USAQ).
Results: Statistical analysis using the Bootstrap method revealed that NML significantly impacts PWB both directly and indirectly through serial mediation by PF and USA. The results revealed a significant indirect effect of NML on PWB through PF and USA (b = -0.013, t = 1.800). Furthermore, the direct effect of NML on PWB in the presence of the mediators was also found to be significant (b = 0.156, P = 0.002).
Conclusion: There is partial serial mediation of PF and USA on the relationship between NML and PWB. This study revealed the crucial role of MML in enhancing PWB through the serial mediation of PF and USA among Generation Z. These findings suggest the potential of targeted digital literacy programs as effective tools for improving mental health in this digitally immersed generation.
Keywords: Media literacy; mental health; psychological wellbeing; students; universities.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Overall and Domain-Specific Psychological Well-Being Between Homemakers and Employed Women: A Cross-Sectional Study From Perambalur District, Tamil Nadu.Cureus. 2024 Dec 4;16(12):e75103. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75103. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39759613 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived Social Support Promotes Nursing Students' Psychological Wellbeing: Explained With Self-Compassion and Professional Self-Concept.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 5;13:835134. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.835134. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35478770 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Physical Activity Levels and Psychological Well-Being Among Male University Students in South East, Nigeria: A Cross-Sectional Study.Am J Mens Health. 2021 Mar-Apr;15(2):15579883211008337. doi: 10.1177/15579883211008337. Am J Mens Health. 2021. PMID: 33899583 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy and Psychological Well-Being: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2025 Jan 20;17(1):e77705. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77705. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39974259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A sequential mediation model of perceived social support, mindfulness, perceived hope, and mental health literacy: An empirical study on Taiwanese university students.Acta Psychol (Amst). 2023 Oct;240:104016. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2023.104016. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Acta Psychol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37729828 Review.
References
-
- Ryff CD. Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1989;56(6):1069–81.
-
- Hernandez-de-Menendez M, Escobar Díaz CA, Morales-Menendez R. Educational experiences with generation. Int J Interact Design Manuf. 2020;14(3):847–59.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources