From the gut to the brain, mechanisms and clinical applications of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on the treatment of anxiety and insomnia
- PMID: 40400620
- PMCID: PMC12093412
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1570173
From the gut to the brain, mechanisms and clinical applications of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on the treatment of anxiety and insomnia
Abstract
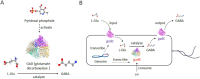
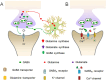
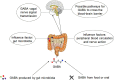
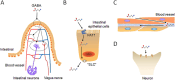
Anxiety and insomnia are prevalent global mood disorders, and affect approximately 4 and 10 out of every 100 individuals, respectively. Common abnormal brain activity and altered neural circuitries are detected in patients with anxiety disorders and insomnia, suggesting overlapping pathogenesis in these two disorders. Promisingly, GABA from dietary supplements and GABA produced by gut microbiota have shown significant treatment effects in anxiety and insomnia. This review summarizes neurological mechanisms causing anxiety and insomnia, reveals cellular pathways transferring GABA from the gut to the brain, and delivers the therapeutic potential of gut derived GABA for anxiety and insomnia. Moreover, this review proposes emerging therapeutic strategies utilizing engineered GABA-producing bacteria to target anxiety and insomnia, and highlights the potential of live biotherapeutics as novel interventions for mood disorders.
Keywords: GABA; anxiety; genetic engineered bacteria; gut microbiota; insomnia; probiotics.
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Chen and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
YC is employed by GeneYoung Biopharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An analysis of electroacupuncture as adjunctive treatment for insomnia: a new perspective targeting GABA-mediated microbiome-gut-brain axis.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1504316. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1504316. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40371088 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention in gut microbiota increases intestinal γ-aminobutyric acid and alleviates anxiety behavior: a possible mechanism via the action on intestinal epithelial cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 5;14:1421791. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1421791. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39301289 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Supplementation with Lactobacillus Probiotics on Insomnia Treatment.Altern Ther Health Med. 2021 Jun;27(S1):178-184. Altern Ther Health Med. 2021. PMID: 33609341
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid in Stress and Depressive Disorders through the Gut-Brain Axis.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 24;11(12):3128. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123128. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a potential postbiotic mediator in the gut-brain axis.NPJ Sci Food. 2024 Apr 2;8(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41538-024-00253-2. NPJ Sci Food. 2024. PMID: 38565567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

