Cerebral ischemia detection using deep learning techniques
- PMID: 40400660
- PMCID: PMC12092319
- DOI: 10.1007/s13755-025-00352-8
Cerebral ischemia detection using deep learning techniques
Abstract
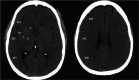
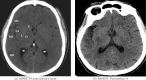
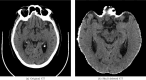
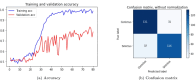
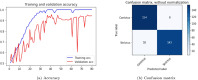
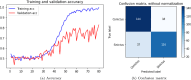
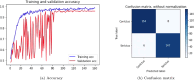
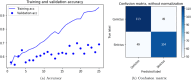
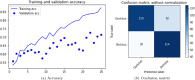
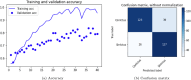
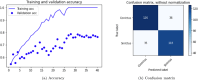
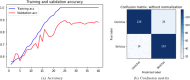
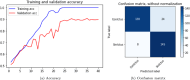
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA), commonly known as stroke, stands as a significant contributor to contemporary mortality and morbidity rates, often leading to lasting disabilities. Early identification is crucial in mitigating its impact and reducing mortality. Non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) remains the primary diagnostic tool in stroke emergencies due to its speed, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. NCCT enables the exclusion of hemorrhage and directs attention to ischemic causes resulting from arterial flow obstruction. Quantification of NCCT findings employs the Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score (ASPECTS), which evaluates affected brain structures. This study seeks to identify early alterations in NCCT density in patients with stroke symptoms using a binary classifier distinguishing NCCT scans with and without stroke. To achieve this, various well-known deep learning architectures, namely VGG3D, ResNet3D, and DenseNet3D, validated in the ImageNet challenges, are implemented with 3D images covering the entire brain volume. The training results of these networks are presented, wherein diverse parameters are examined for optimal performance. The DenseNet3D network emerges as the most effective model, attaining a training set accuracy of 98% and a test set accuracy of 95%. The aim is to alert medical professionals to potential stroke cases in their early stages based on NCCT findings displaying altered density patterns.
Keywords: Cerebral ischemia; Computed tomography; Deep learning; Ictus dataset; Transfer learning.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DGA3-Net: A parameter-efficient deep learning model for ASPECTS assessment for acute ischemic stroke using non-contrast computed tomography.Neuroimage Clin. 2023;38:103441. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103441. Epub 2023 May 19. Neuroimage Clin. 2023. PMID: 37224605 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary study of time maximum intensity projection computed tomography imaging for the detection of early ischemic change in patient with acute ischemic stroke.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Mar;97(9):e9906. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009906. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29489691 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability, Reproducibility and Prognostic Accuracy of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score on CT Perfusion and Non-Contrast CT in Hyperacute Stroke.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;44(3-4):195-202. doi: 10.1159/000479707. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28810259
-
Computational Image Analysis of Nonenhanced Computed Tomography for Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Systematic Review.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 May;29(5):104715. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104715. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32144071
-
Non-contrast Computed Tomography in Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Pictorial Review.Med J Malaysia. 2013;68(1):93-100. Med J Malaysia. 2013. PMID: 23466782 Review.
References
-
- Antón-Munárriz C, Pastor-Vargas R, Haut JM, et al (2023) Detection of cerebral ischaemia using transfer learning techniques. In: 2023 IEEE 36th international symposium on computer-based medical systems (CBMS), pp 589–59. 10.1109/CBMS58004.2023.00284
-
- Ramos MM, Giadas TC. Evaluación vascular en el código ictus: papel de la angio-tomografía computarizada. Radiologia. 2015;57(2):156–66. - PubMed
-
- Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, et al. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. Lancet. 2000;355(9216):1670–4. - PubMed
-
- Lisowska A, O’Neil A, Dilys V, et al (2017) Context-aware convolutional neural networks for stroke sign detection in non-contrast ct scans. In: Annual conference on medical image understanding and analysis, Springer, pp 494–505
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

