Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Kidney Injury: Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 40400780
- PMCID: PMC12094478
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S519345
Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Kidney Injury: Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
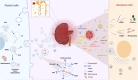
Acute kidney injury (AKI) has a high morbidity and mortality rate but can only be treated with supportive therapy in most cases. The diagnosis of AKI is mainly based on serum creatinine level and urine volume, which cannot detect kidney injury sensitive and timely. Therefore, new diagnostic and therapeutic molecules of AKI are being actively explored. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), secreted by almost all cells, can originate from different parts of the kidney and mediate intercellular communication between various cell types of nephrons. At present, numerous successful EV-based biomarker discoveries and treatments for AKI have been made, such as the confirmed diagnostic role of urine-derived EVs in AKI and the established therapeutic role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived EVs in AKI have been confirmed; however, these related studies lack a full discussion. In this review, we summarize the latest progression in the profound understanding of the functional role of EVs in AKI caused by various etiologies in recent years and provide new insights into EVs as viable biomarkers and therapeutic molecules for AKI patients. Furthermore, the current challenges and prospects of this research area are briefly discussed, presenting a comprehensive overview of the growing foregrounds of EVs in AKI.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; diagnostic biomarkers; extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stem cells; therapeutic molecules.
© 2025 Yan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Kidney Injury and Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 18;22(16):8913. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168913. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Acute Kidney Injury: Potential Therapeutic Avenue for Renal Repair and Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 30;23(7):3792. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073792. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oct-4 Enhanced the Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Kidney Injury.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2020;45(1):95-108. doi: 10.1159/000504368. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2020. PMID: 31927554
-
Extracellular vesicles from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance the recovery of acute kidney injury.Cytotherapy. 2024 Jan;26(1):51-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2023.09.003. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Cytotherapy. 2024. PMID: 37843481
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to the Rescue of Renal Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 20;22(12):6596. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126596. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- KDIGO Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2(1):1. doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

