Development and validation of a nomogram to predict the risk of post-stroke complex regional pain syndrome
- PMID: 40400911
- PMCID: PMC12092387
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1577256
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict the risk of post-stroke complex regional pain syndrome
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to assess risk factors and build a nomogram model to facilitate the early recognition of post-stroke complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS).
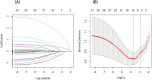
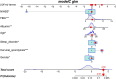
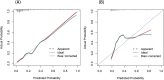
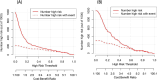
Methods: A total of 587 stroke patients admitted to Dongguan Hospital of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from September 2021 to October 2024 were initially included in this study. After exclusions, 376 patients were selected. Among these, there were 90 patients with post-stroke CRPS, while the non-stroke CRPS group consisted of 286 patients. Feature selection and optimization to generate the predictive model and nomogram were performed using LASSO regression and multivariable logistic regression analysis. We also utilized calibration plots, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, decision curves (DCA), and clinical impact curves (CIC) for model validation.
Results: LASSO regression analysis and multivariate logistic regression identified gender, age, NIHSS score, cervical spondylosis, sleep disorders, fasting blood glucose (FBG), and albumin (ALB) as significant predictors. The nomogram model showcased reliable predictive effectiveness, achieving an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.858 (95% CI, 0.801-0.915). Both DCA and CIC demonstrated that the nomogram model holds substantial clinical utility.
Conclusion: This study has developed a novel predictive model for post-stroke CRPS, providing a valuable tool to facilitate the early detection of high-risk patients in a clinical environment.
Keywords: LASSO; nomogram; post-stroke complex regional pain syndrome; prediction model; stroke.
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Song, Deng, Cheng, Xue and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A novel nomogram based on the patient's clinical data and CT signs to predict poor outcomes in AIS patients.PeerJ. 2025 Jan 6;13:e18662. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18662. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39790454 Free PMC article.
-
Development, assessment and validation of a novel nomogram model for predicting stroke mimics in stroke center:A single-center observational study.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 27;10(19):e38602. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38602. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39403531 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of cellular analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in distinguishing pulmonary infectious and non-infectious diseases in patients with pulmonary shadow.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 20;11:1496088. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1496088. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39635594 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting colorectal cancer risk: a novel approach using anemia and blood test markers.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 22;14:1347058. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1347058. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38344199 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for predicting neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A retrospective study.Neurourol Urodyn. 2024 Nov;43(8):2157-2168. doi: 10.1002/nau.25536. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Neurourol Urodyn. 2024. PMID: 38962959
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

