Phenotypes and endotypes in bronchiectasis: a narrative review of progress toward precision medicine
- PMID: 40400921
- PMCID: PMC12090171
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-2024-1945
Phenotypes and endotypes in bronchiectasis: a narrative review of progress toward precision medicine
Abstract
Background and objective: Bronchiectasis, which was previously regarded as a rare condition, has recently attracted increased attention with advancements in research and therapeutic strategies. However, heterogeneity remains a major challenge in the management of bronchiectasis. This review aims to elucidate the concepts of phenotypes and endotypes, facilitate a deeper understanding of bronchiectasis complexity, and pave the way for personalized treatment approaches.
Methods: The PubMed database was searched for relevant articles published in English between January 1990 and August 2024 using keywords "bronchiectasis", "phenotype", "endotype", "diagnosis", "disease management", "complexity", "eosino*", "neutrop*", and "precision medicine".
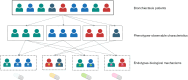
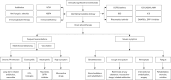
Key content and findings: We examined established clinical phenotypes, such as frequent exacerbator and chronic airway disease overlap, which significantly influence prognosis and therapeutic management. The significance of etiology-based phenotyping was also discussed while emphasizing how identifying specific underlying causes can guide targeted therapies. We further explored recent advancements in characterising bronchiectasis endotypes, particularly those marked by neutrophilic and eosinophilic inflammation. These endotypes provide valuable insights into underlying pathophysiological mechanisms and guide the selection of clinical management strategies. Recent cluster analysis research has identified distinct inflammatory endotypes in bronchiectasis, thereby improving the understanding of disease progression and identifying potential therapeutic targets. Integrating molecular endotyping with clinical phenotyping provides a more comprehensive perspective of the disease, underscoring the necessity of a dual approach to effectively address its inherent heterogeneity. Furthermore, we emphasize the significance of identifying treatable traits within these frameworks, which can enhance the precision of treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes. By exploring the interplay between clinical phenotypes, endotypes, and patient-specific characteristics, this review highlights the potential for advancing precision medicine for bronchiectasis.
Conclusions: Enhancing our understanding of bronchiectasis through these concepts is essential for developing tailored interventions that target the underlying biological mechanisms, thereby improving disease management and patients' quality of life.
Keywords: Bronchiectasis; disease management; endotype; phenotype; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-2024-1945/coif). The series “Frontiers in Bronchiectasis Management: Translational Science and Practice” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. H.C. reports grant from the Basic Science Research Program of the Korean Ministry of Education (grant No. 2021R1I1A3052416); lecture fees from Boryung Pharmaceutical Co., Kolon Pharma and Abbott. Y.H.G. reports grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 82270047) and Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project (grant No. 2024ZD0529700). The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Choi H, Chalmers JD. Bronchiectasis: from orphan disease to precision medicine. In: Wagner TOF, Humbert M, Wijsenbeek M, et al., eds. Rare Diseases of the Respiratory System (ERS Monograph). Sheffield: European Respiratory Society; 2023:150-64.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
