Causal relationship between serum metalloproteinase 12 levels and aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 40400971
- PMCID: PMC12090172
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-2025-377
Causal relationship between serum metalloproteinase 12 levels and aortic dissection and aortic aneurysm: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Background: Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12) levels have been shown to be elevated in patients with aortic dissection (AD) and aortic aneurysm (AA). However, whether MMP-12 is associated with AD and AA has not been conclusively examined. The aim of this study was to clarify the role of MMP-12 in AD and AA formation and to verify the correlation between MMP-12 and AD and AA development at the gene level via Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
Methods: The data for analyzing MMP-12 gene mutations were obtained from the Integrative Epidemiology Unit (IEU) OpenGWAS database, which includes data from 21,758 European residents. Data on the genetic variation of AD and AA were retrieved from the FinnGen database. In the forward MR analysis, we evaluated the causal effect of MMP-12 on AD and AA. Subsequently, the causal association of AD and AA with MMP-12 was investigated in the reverse MR study. The inverse-variance weighting (IVW) method was the principal statistical technique used in this study.
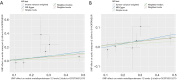
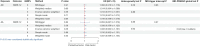
Results: In the forward MR analysis, the IVW results showed that serum MMP-12 levels were positively related to an increased risk of AD [odds ratio (OR) =1.301; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.002-1.697; P=0.048] and AA (OR =1.121; 95% CI: 1.007-1.248; P=0.04). For the reverse MR studies, no genetic relationships were observed between AD or AA and MMP-12 levels, nor was any heterogeneity or pleiotropy.
Conclusions: There was a correlation between serum MMP-12 and the risk of AD and AA. MMP-12 may be a potential therapeutic target for AD and AA.
Keywords: Matrix metalloproteinase-12 (MMP-12); Mendelian randomization (MR); aortic aneurysm (AA); aortic dissection (AD).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-2025-377/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
