Comparative Efficacy of Nutritional Supplements in Modulating Lung Function and Exercise Capacity in COPD Patients: A Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40401105
- PMCID: PMC12094480
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S517252
Comparative Efficacy of Nutritional Supplements in Modulating Lung Function and Exercise Capacity in COPD Patients: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effects of nutritional supplements on lung function and exercise tolerance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
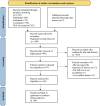
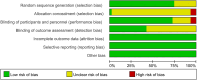
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on nutritional supplements in COPD patients, with the search ending December 31, 2023. Two authors independently screened studies, extracted data, and assessed quality using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Data were analyzed using RevMan 5.4 and R 4.2.3.
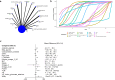
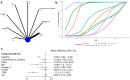
Results: Forty-eight studies with 2481 COPD patients were included. Network meta-analysis showed six supplements significantly improved the 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) (all p<0.05), with the top three being: Coenzyme Q10+ Creatine [MD=63, 95% CI (36, 90)], L-carnitine [MD=53, 95% CI (24, 82)], and anabolic steroids [MD=44, 95% CI (7.1, 82)]. Four supplements improved FEV1%(all p<0.05): nanocurcumin [MD=13, 95% CI (7.7, 18)], Vitamin D [MD=7.5, 95% CI (5.1, 9.9)], probiotics [MD=7.1, 95% CI (5.2, 9.1)] and BSO [MD=4.9, 95% CI (1.6, 8.3)]. In pairwise comparisons, nanocurcumin outperformed BSO and Probiotics. Nanocurcumin [MD=12, 95% CI (4.6, 19), p<0.05] improved FEV1/FVC, and nitrate [MD=26, 95% CI (9.7, 42), p<0.05] was effective for the Incremental Shuttle Walk Test (ISWT). Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) products [MD=-1.3, 95% CI (-1.9, -0.67)], melatonin (MLT) [MD=-0.9, 95% CI (-1.6, -0.21)] and Calcitriol [MD=-0.66, 95% CI (-0.93, -0.39)] improved the modified Medical Research Council(mMRC) dyspnea score (all p<0.05), with comparable efficacy among them.
Conclusion: Nutritional supplements improve lung function and exercise endurance in COPD. Coenzyme Q10+Creatine is most effective for endurance, while Nanocurcumin has the greatest impact on lung function.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; exercise endurance; lung function; network meta-analysis; nutritional supplements.
© 2025 Zeng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of various nutritional supplements in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a network meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 8;25(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03667-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40340688 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Virtual Reality-Complemented Pulmonary Rehabilitation on Lung Function, Exercise Capacity, Dyspnea, and Health Status in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Apr 7;27:e64742. doi: 10.2196/64742. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40193185 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 23;2015(2):CD003793. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003793.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25705944 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplementation for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD000998. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000998.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235577 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated disease management interventions for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 10;(10):CD009437. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009437.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 8;9:CD009437. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009437.pub3. PMID: 24108523 Updated.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

