Prognostic value of lactate clearance, fluid balance, and APACHE II score in patients with cardiogenic shock receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- PMID: 40401225
- PMCID: PMC12092362
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1557909
Prognostic value of lactate clearance, fluid balance, and APACHE II score in patients with cardiogenic shock receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study is to examine the prognostic value of lactate clearance, fluid balance, and the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score in patients with cardiogenic shock undergoing treatment with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
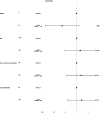
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 32 patients with cardiogenic shock who underwent ECMO in the Intensive Care Unit of Peking University International Hospital between January 2021 and June 2024. The patients were categorized into a survival group (n = 14) and a non-survival group (n = 18) based on their clinical outcomes. Baseline characteristics, including age, sex, and body weight and so on were collected for both groups. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors influencing patient prognosis. The prognostic value of relevant indicators was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, while Pearson's correlation analysis was conducted to assess the relationships between specific indicators.
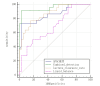
Results: Lactate clearance was significantly lower in the non-survival group compared to the survival group, while fluid balance and APACHE II scores were notably higher in the non-survival group (p < 0.05). Based on the predictive model, the APACHE II score demonstrated the highest specificity for prognosis at 97.4%, whereas the combined indices exhibited the highest sensitivity at 95.5%. Additionally, lactate clearance revealed a negative correlation with both fluid balance and APACHE II scores (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: This pilot study demonstrated that lactate clearance, fluid balance, and APACHE II score are valuable prognostic indicators for patients; however, the predictive accuracy of individual indicators is limited. The combined assessment of these indices provides a more robust and reliable predictive performance.
Keywords: APACHE II score; cardiogenic shock; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy; fluid balance; lactate clearance.
© 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Li, Guo, Qi, Xing and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Prognostic value of oxygen challenge test for patients with cardiogenic shock receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Dec;29(12):1102-1106. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.12.010. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 29216944 Chinese.
-
[Prognostic significance of early lactate clearance rate for severe acute respiratory failure patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;37(3):197-201. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24809711 Chinese.
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
[Value of cardiac troponin T in predicting the prognosis of patients with cardiogenic shock receiving veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment: a consecutive 5-year retrospective study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Sep;32(9):1091-1095. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200630-00494. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33081896 Chinese.
-
Predicting In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Therapy.Cardiorenal Med. 2025;15(1):164-173. doi: 10.1159/000543434. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Cardiorenal Med. 2025. PMID: 39778556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kunkel JB, Holle SLD, Hassager C, Pecini R, Wiberg S, Palm P, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor antibodies (tocilizumab) in acute myocardial infarction with intermediate to high risk of cardiogenic shock development (DOBERMANN-T): study protocol for a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, single-center, randomized clinical trial. Trials. (2024) 25(1):739. 10.1186/s13063-024-08573-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holle SLD, Kunkel JB, Hassager C, Pecini R, Wiberg S, Palm P, et al. Low-dose dobutamine in acute myocardial infarction with intermediate to high risk of cardiogenic shock development (the DOBERMANN-D trial): study protocol for a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, single-center, randomized clinical trial. Trials. (2024) 25(1):731. 10.1186/s13063-024-08567-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardiovascular Emergency and Critical Care Group, Cardiovascular Disease Branch, Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Committee of Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Disease. Chinese expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of cardiogenic shock (2018). Chin J Cardiovasc Dis. (2019) 47(4):265–77. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2019.04.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

