Global Epidemiology of Early-Onset Digestive System Malignancy: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
- PMID: 40401498
- PMCID: PMC12136802
- DOI: 10.1111/jgh.17012
Global Epidemiology of Early-Onset Digestive System Malignancy: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract
Background and aim: The researches on the global burden of digestive system malignancy in young populations were limited. This study aimed to comprehensively investigate the burden of early-onset digestive system malignancy (often defined as cancers diagnosed below the age of 50) based on the Global Burden of Disease 2021.
Methods: Data of incidence, prevalence, deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and risk factors for the five major early-onset digestive system malignancies, including early-onset esophageal cancer (EOEC), early-onset gastric cancer (EOGC), early-onset liver cancer (EOLC), early-onset pancreatic cancer (EOPC), and early-onset colorectal cancer (EOCRC), were extracted from GBD 2021. The average annual percent change (AAPC) was calculated using joinpoint regression analysis. The Bayesian age-period-cohort (BAPC) model was utilized to predict the burden up to 2030.
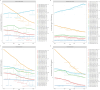
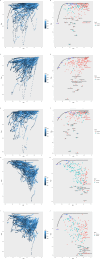
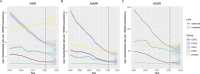
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of early-onset digestive system malignancies, except for EOCRC (AAPC, 0.37), showed a decreasing pattern. Meanwhile, the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and age-standardized DALYs rate (ASDR) of early-onset digestive system malignancy presented a downward trend. Notably, high-middle sociodemographic index (SDI) countries experienced higher disease burdens. Dietary risk factors, tobacco, alcohol consumption, and metabolic factors were the main risk factors. The ASIR of EOEC and EOCRC was projected to increase in 2030, whereas the trend for EOGC, EOLC, and EOPC was projected to decrease.
Conclusions: Early-onset digestive system malignancy presented notable heterogeneity across gender, geography, and cancer types. This emphasizes the urgency of addressing the public health challenge of early-onset digestive system malignancy.
Keywords: early‐onset digestive system malignancy; epidemiology; risk factor; trend in global burden.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology published by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., et al., “Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today,” (2020), 20182020.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021MHZ040/Natural Science Research Project of Minhang District in Shanghai
- 2020MHJC02/School-level Project of Minhang Central Hospital
- 8217100675/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024MZYS16/Minhang District medical teaching and research collaborative health service system under the high-level specialist backbone physician training project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

