Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Single-Dose Dazukibart in Healthy Adults in China and Japan: Results From 2 Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 1 Studies
- PMID: 40401504
- PMCID: PMC12314112
- DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.1522
Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Single-Dose Dazukibart in Healthy Adults in China and Japan: Results From 2 Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 1 Studies
Abstract
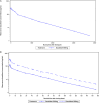
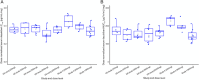
Dazukibart is a humanized monoclonal antibody selectively targeting interferon-β. The pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of dazukibart were evaluated in 2 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-dose, Phase 1 studies in healthy adults in China (Study 1: N = 18; dazukibart 900 mg = 15; placebo = 3) and Japan (Study 2: N = 12; Cohort 1: dazukibart 300 mg = 5, placebo = 1; and Cohort 2: dazukibart 900 mg = 5, placebo = 1). PK parameters were assessed after dosing in Study 1 and Study 2, and no significant differences were observed between PK findings among participants in both studies. A biphasic decline in dazukibart serum concentrations was observed in both studies. Exposures increased dose proportionally in Study 2. Body weight, but not race, was identified as an independent covariate of exposure using population PK modeling (including data from a Phase 1 US study [NCT02766621]). No deaths/discontinuations or serious/severe adverse events were observed, mostly mild adverse events were reported. No participants in Study 1 were antidrug antibody positive; 20.0% in Study 2 were positive for treatment-induced antidrug antibodies and neutralizing antibodies. PK parameters and immunogenicity rates were consistent with the US study, and no new safety signals were identified.
Keywords: dazukibart; ethnic sensitivity; interferon‐β; pharmacokinetics; safety.
© 2025 Pfizer Inc. Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Clinical Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
Naihan Chen, Yamato Sano, Shuiyi Hu, Junichi Tabira, Xin Luo, Hiroki Yoshimatsu, John Prybylski and Myron Chu are employees of Pfizer and hold Pfizer stocks. Xiaohong Wang and Haiyan Li are employees of Peking University Third Hospital. Kenji Takazawa is an employee of Shinanozaka Clinic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy, safety, and target engagement of dazukibart, an IFNβ specific monoclonal antibody, in adults with dermatomyositis: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial.Lancet. 2025 Jan 11;405(10473):137-146. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)02071-3. Lancet. 2025. PMID: 39798982 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of Axatilimab in Healthy Japanese Male Participants: Results from a Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blind, Dose-Escalation Study.Clin Drug Investig. 2025 Jun;45(6):327-334. doi: 10.1007/s40261-025-01438-7. Epub 2025 May 17. Clin Drug Investig. 2025. PMID: 40381116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Donanemab in Healthy Chinese Participants: A Phase 1, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2025 Aug;14(8):598-604. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.1533. Epub 2025 May 16. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2025. PMID: 40377397 Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-IL-12/23p40 antibodies for induction of remission in Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 5;(5):CD007572. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007572.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 25;11:CD007572. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007572.pub3. PMID: 25942580 Updated.
-
Anti-IL-12/23p40 antibodies for induction of remission in Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 25;11(11):CD007572. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007572.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 May 13;5:CD007572. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007572.pub4. PMID: 27885650 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Bilgic H, Ytterberg SR, Amin S, et al. Interleukin‐6 and type I interferon–regulated genes and chemokines mark disease activity in dermatomyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(11):3436‐3446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

