Targeting COL5A1 enhances anoikis thus attenuating malignancy of glioblastoma via inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- PMID: 40402199
- PMCID: PMC12198276
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-025-05036-7
Targeting COL5A1 enhances anoikis thus attenuating malignancy of glioblastoma via inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Abstract
Purpose: As one of the most prevalent primary brain tumors, glioblastoma (GBM) is characterized by its severe malignancy and extremely poor prognosis. Recent studies have demonstrated that targeting anoikis and malignancy showed impressed efficiency for treatment in a wide range of solid tumors, however, relevant research on GBM still remains unclarified.
Methods: In this study, genes related with malignancy and anoikis of GBM were identified by utilizing the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA) and the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB). Subsequently, the role of the key gene was validated via proliferation, invasion and migration experiments both in conditions with and without attachment. Moreover, RNA sequencing analysis was employed to reveal further mechanisms.
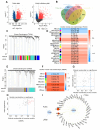
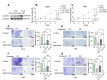
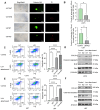
Results: Here, Type V collagen alpha 1 (COL5A1) was identified as a critical gene associated with anoikis and poor outcomes. Additionally, COL5A1 knockdown induced significant reduction in malignancy of GBM both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, cell anoikis was remarkable enhanced by reduced expression of COL5A1 after low-attachment cell culture. Mechanically, RNA sequencing analysis revealed that the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was diminished following COL5A1 knockdown, which indicated that COL5A1 reduced anoikis via regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway thus promoted malignancies of GBM cells.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrated the novel evidence that COL5A1 serves as an essential regulatory factor influencing both anoikis and malignancy of GBM cells by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, indicating that COL5A1 could be a novel prognosis-related biomarker and potential therapeutic target for GBM.
Keywords: COL5A1; Anoikis; Glioblastoma; Malignancy; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: All utilization of animals and GBM tissue samples in this study were approved by the Scientific Ethics Committee at the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (approve no. 2021 − 695). Informed Consent: All tissue samples have obtained necessary consent. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autophagy-related CMTM6 promotes glioblastoma progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway and acts as an onco-immunological biomarker.J Gene Med. 2024 May;26(5):e3685. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3685. J Gene Med. 2024. PMID: 38686653
-
Exosomal circ_0001583 Drives Glioblastoma Cell Advancement Through the miR-647/CKAP2L Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10687-10706. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04875-9. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40229458 Free PMC article.
-
SENP1-Mediated deSUMOylation Regulates the Tumor Remodeling of Glioma Stem Cells Under Hypoxic Stress.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241257490. doi: 10.1177/15330338241257490. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38803001 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Molecular Targeted Therapies for Adult-Type Diffuse Glioma: An Analysis of Clinical and Laboratory Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 21;24(13):10456. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310456. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445633 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Omuro A, DeAngelis LM (2013) Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA 310:1842–1850. 10.1001/jama.2013.280319 - PubMed
-
- Berger TR, Wen PY, Lang-Orsini M, Chukwueke UN (2022) World health organization 2021 classification of central nervous system tumors and implications for therapy for Adult-Type gliomas: A review. JAMA Oncol 8:1493–1501. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.2844 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

