High-affinity CD16A polymorphism associated with reduced risk ofsevere COVID-19
- PMID: 40402577
- PMCID: PMC12306582
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.191314
High-affinity CD16A polymorphism associated with reduced risk ofsevere COVID-19
Abstract
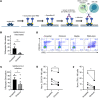
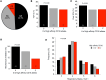
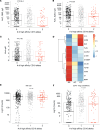
CD16A is an activating Fc receptor on NK cells that mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), a key mechanism in antiviral immunity. However, the role of NK cell-mediated ADCC in SARS-CoV-2 infection remains unclear, particularly whether it limits viral spread and disease severity or contributes to the immunopathogenesis of COVID-19. We hypothesized that the high-affinity CD16AV176 polymorphism influences these outcomes. Using an in vitro reporter system, we demonstrated that CD16AV176 is a more potent and sensitive activator than the common CD16AF176 allele. To assess its clinical relevance, we analyzed 1,027 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from the Immunophenotyping Assessment in a COVID-19 cohort (IMPACC), a comprehensive longitudinal dataset with extensive transcriptomic, proteomic, and clinical data. The high-affinity CD16AV176 allele was associated with a significantly reduced risk of ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, and severe disease trajectories. Lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG titers were correlated to CD16AV176; however, there was no difference in viral load across CD16A genotypes. Proteomic analysis revealed that participants homozygous for CD16AV176 had lower levels of inflammatory mediators. These findings suggest that CD16AV176 enhances early NK cell-mediated immune responses, limiting severe respiratory complications in COVID-19. This study identifies a protective genetic factor against severe COVID-19, informing future host-directed therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cellular immune response; Immunology; Innate immunity; NK cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19 AI090023/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026940/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI062629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI146581/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI118610/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI128910/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104870/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA018926/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI125357/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI145835/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI146581/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005023/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U19 AI128913/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI118608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM141323/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI142766/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025482/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI122220/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI077439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI135803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

