The patient-specific mouse model with Foxg1 frameshift mutation provides insights into the pathophysiology of FOXG1 syndrome
- PMID: 40404610
- PMCID: PMC12099012
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59838-4
The patient-specific mouse model with Foxg1 frameshift mutation provides insights into the pathophysiology of FOXG1 syndrome
Abstract
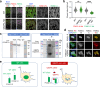
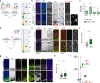
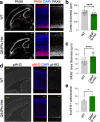
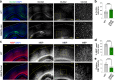
Single allelic mutations in the FOXG1 gene lead to FOXG1 syndrome (FS). To understand the pathophysiology of FS, which vary depending on FOXG1 mutation types, patient-specific animal models are critical. Here, we report a patient-specific Q84Pfs heterozygous (Q84Pfs-Het) mouse model, which recapitulates various FS phenotypes across cellular, brain structural, and behavioral levels. Q84Pfs-Het cortex shows dysregulations of genes controlling cell proliferation, neuronal projection and migration, synaptic assembly, and synaptic vesicle transport. The Q84Pfs allele produces the N-terminal fragment of FOXG1 (Q84Pfs protein) in Q84Pfs-Het mouse brains, which forms intracellular speckles, interacts with FOXG1 full-length protein, and triggers the sequestration of FOXG1 to distinct subcellular domains. Q84Pfs protein promotes the radial glial cell identity and suppresses neuronal migration in the cortex. Our study uncovers the role of the FOXG1 fragment from FS-causing FOXG1 variants and identifies the genes involved in FS-like cellular and behavioral phenotypes, providing insights into the pathophysiology of FS.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Elise Brimble is a salaried employee of Citizen Health and holds vested and unvested stock options. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
The patient-specific mouse model with Foxg1 frameshift mutation uncovers the pathophysiology of FOXG1 syndrome.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 2:rs.3.rs-2953760. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2953760/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 22;16(1):4760. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59838-4. PMID: 37398410 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The patient-specific mouse model with Foxg1 frameshift mutation provides insights into the pathophysiology of FOXG1 syndrome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 22:2025.01.21.634140. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.21.634140. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 22;16(1):4760. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59838-4. PMID: 39896554 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

