Innovative vibriosis control in open aquaculture: Paratapes undulata as a sustainable growth and resistance enhancer in red tilapia
- PMID: 40404688
- PMCID: PMC12098663
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-01026-x
Innovative vibriosis control in open aquaculture: Paratapes undulata as a sustainable growth and resistance enhancer in red tilapia
Abstract
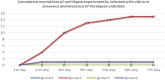
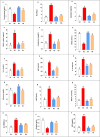
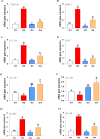
This study demonstrates the novel therapeutic potential of Paratapes undulata for mitigating Vibrio alginolyticus infection in red tilapia. In vivo, P. undulata significantly improved growth by approximately 362% in group G3 (Clam-treated Control) and 284% in group G4 (Clam-treated Infected), compared to the infected control group (G2), and reduced mortality by 100% in group G3 and 75% in group G4, compared to the infected control group (G2), and alleviated clinical signs, correlating with enhanced hematological and biochemical profiles, and reduced tissue damage. Mechanistically, P. undulata modulated the immune response by shifting cytokine balance towards anti-inflammation, enhanced antioxidant capacity, and directly inhibited Vibrio alginolyticus virulence. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy analyses revealed the presence of bioactive compounds contributing to these effects. These findings establish P. undulata as a promising, natural, and sustainable biocontrol agent for vibriosis in aquaculture, offering a novel strategy for disease management and reducing reliance on antibiotics. This study suggests that P. undulata can be effectively incorporated into aquaculture feed or water treatments to prevent and manage vibriosis outbreaks.
Keywords: Paratapes undulata; Vibrio alginolyticus; Aquaculture immunology; Natural antimicrobials; Probiotic aquaculture.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Treatment Trial of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Experimentally Infected with Vibrio alginolyticus Isolated from Sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax).Pak J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan;23(12):1591-1600. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2020.1591.1600. Pak J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33274891
-
Isolation, characterization and genomic analysis of bacteriophages for biocontrol of vibriosis caused by Vibrio alginolyticus.Virus Res. 2025 Mar;353:199529. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2025.199529. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Virus Res. 2025. PMID: 39914594 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and pathogenicity of Vibrio alginolyticus SWS causing high mortality in mud crab (Scylla serrata) aquaculture in Hong Kong.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 23;14:1425104. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1425104. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39108984 Free PMC article.
-
Cold-water vibriosis. The current status of knowledge.J Fish Dis. 2017 Jan;40(1):119-126. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12465. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Fish Dis. 2017. PMID: 27072873 Review.
-
Vibriosis in Fish: A Review on Disease Development and Prevention.J Aquat Anim Health. 2019 Mar;31(1):3-22. doi: 10.1002/aah.10045. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Aquat Anim Health. 2019. PMID: 30246889 Review.
References
-
- Mishra, A., Kim, H. S., Kumar, R. & Srivastava, V. (2024) Advances in Vibrio-related infection management: An integrated technology approach for aquaculture and human health. Critic. Rev. Biotechnol.10(1080/07388551), 2336526 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Haenen, O. L. M. et al. Bacterial diseases of tilapia, their zoonotic potential and risk of antimicrobial resistance. Rev. Aquaculture10.1111/raq.12743 (2023).
-
- Jantrakajorn, S., Maisak, H. & Wongtavatchai, J. Comprehensive Investigation of Streptococcosis Outbreaks in Cultured Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus, and Red Tilapia Oreochromis sp of Thailand. J. World Aquac Soc.45, 392 (2014).
-
- El-Sayed, M. E., Algammal, A. M., Abouel-Atta, M. E., Mabrok, M. & Emam, A. M. Pathogenicity, genetic typing, and antibiotic sensitivity of Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia zillii. Rev. Med. Vet. (Toulouse)170, 80–86 (2019).
-
- Saad, M. F., Elsayed, M. M., Khder, M., Abdelaziz, A. S. & El-Demerdash, A. S. Biocontrol of multidrug resistant pathogens isolated from fish farms using silver nanoparticles combined with hydrogen peroxide insight to its modulatory effect. Sci. Rep.14, 791. 10.1038/s41598-024-58349-4 (2024). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

