KK2845, a PBD dimer-containing antibody-drug conjugate targeting TIM-3-expressing AML
- PMID: 40404985
- PMCID: PMC12310520
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-025-02642-2
KK2845, a PBD dimer-containing antibody-drug conjugate targeting TIM-3-expressing AML
Abstract
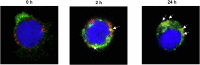
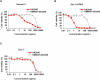
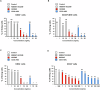
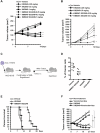
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a common hematopoietic malignancy with high recurrence rates, and there is an urgent need for new therapeutic agents. T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 (TIM-3) is expressed on the surface of both LSCs and blasts in most AML patients, but not in normal hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). We have developed KK2845, an antibody drug conjugate (ADC) that consists of an anti-TIM-3 fully human IgG1 antibody, a valine-alanine linker and a highly potent DNA cross-linking pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer SG3199. KK2845 exhibited potent cytotoxicity against AML cells both in vitro and in vivo. The cytotoxicity against AML cells was almost comparable between KK2845 and CD33-ADC, an anti-CD33 antibody conjugated with PBD dimer that has shown high remission rates in clinical studies. In addition to the cytotoxicity depending on PBD dimer, KK2845 also showed potent antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity against AML cells. KK2845 showed less cytotoxicity against human normal bone marrow cells than CD33-ADC. The pharmacokinetics of KK2845 in cynomolgus monkey after intravenous infusion demonstrated a favorable profile. Taken together, these data suggest that KK2845 could be a novel ADC therapeutic in AML.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.Z., H.K., S.T., T.I., T.A., K.N., S.K., M.A., H.T., and H.S. are employees of Kyowa Kirin. T.S., Y.K., and K.A. are collaborators who received financial support from Kyowa Kirin. Ethics statement: The use of human-derived materials was approved by the Research Ethics Review Committee of Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Kyushu University, or the vendor’s ethical regulations. Informed consent was obtained from all human subjects. All experiments involving animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and performed in accordance with the animal welfare guidelines of Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., and Shin Nippon Biomedical Laboratories, Ltd., both of which are accredited by AAALAC International.
Figures



References
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3:730. - PubMed
-
- Hope KJ, Jin L, Dick JE. Acute myeloid leukemia originates from a hierarchy of leukemic stem cell classes that differ in self-renewal capacity. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:738–43. - PubMed
-
- Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B, Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, et al. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 1994;367:645–8. - PubMed
-
- Shimony S, Stahl M, Stone RM. Acute myeloid leukemia: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2023;98:502–26. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

