NIR-responsive cisplatin nanoparticles for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40406013
- PMCID: PMC12097326
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra01910a
NIR-responsive cisplatin nanoparticles for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
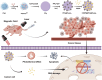
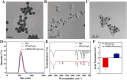
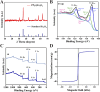
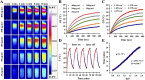
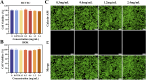
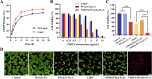
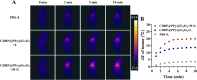
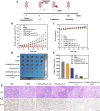
The typically occurring malignant tumor in the head and neck is oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), which is highly aggressive and invasive. Despite surgical advancements, radiation, and chemotherapy, the prognosis for OSCC is still poor. Chemotherapy's effectiveness is frequently restricted by its serious side effects and the development of resistance. In this study, a cisplatin (CDDP)-loaded magnetic targeting nanoplatform (CDDP@PPy@Fe3O4) has been designed for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. PPy with carboxyl groups was first prepared by chemical oxidative polymerization. Then, Fe3O4 nanoparticles were synthesized in situ on its surface and loaded with CDDP through a reaction with the carboxyl groups. The CDDP@PPy@Fe3O4 nanocomposite serves not only as a nanocarrier for the targeted delivery of CDDP to alleviate the systemic toxicity of chemotherapy but also possesses excellent photothermal conversion properties, generating localized heat upon near-infrared laser irradiation that enables photothermal therapy. Contrary to using only chemotherapy or photothermal therapy, CDDP@PPy@Fe3O4 nanoparticles combined with NIR exposure exert superior anticancer effects against OSCC both in vivo and in vitro while exhibiting minimal side effects. Therefore, CDDP@PPy@Fe3O4 nanoparticles could be a promising candidate for nanomedicine in OSCC combination therapy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Targeted and pH-Responsive Nano-Graphene Oxide Nanoparticle Loaded with Doxorubicin for Synergetic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Jun 17;18:3309-3324. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S402249. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37351329 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Multimodal NIR-II Nanoprobe for the Detection of Metastatic Lymph Nodes and Targeting Chemo-Photothermal Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Theranostics. 2019 Jan 1;9(2):391-404. doi: 10.7150/thno.30268. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 30809282 Free PMC article.
-
A light-controllable specific drug delivery nanoplatform for targeted bimodal imaging-guided photothermal/chemo synergistic cancer therapy.Acta Biomater. 2018 Oct 15;80:308-326. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.09.024. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 30240955
-
Multifunctional HNT@Fe3O4@PPy@DOX Nanoplatform for Effective Chemo-Photothermal Combination Therapy of Breast Cancer with MR Imaging.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020 Jun 8;6(6):3361-3374. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01709. Epub 2020 May 27. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020. PMID: 33463181
-
pH and NIR-light-responsive magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death induced by chemo-photothermal therapy.Int J Pharm. 2017 Oct 5;531(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.07.014. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28689965
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

