Dynamics and immunological signature of γδ T cells following antiretroviral therapy initiation in acute HIV-1 Infection
- PMID: 40406103
- PMCID: PMC12095004
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1554916
Dynamics and immunological signature of γδ T cells following antiretroviral therapy initiation in acute HIV-1 Infection
Abstract
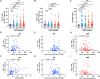
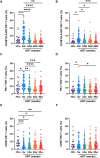
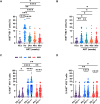
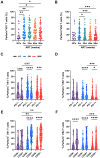
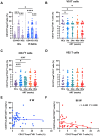
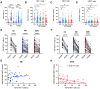
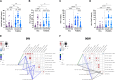
Early antiretroviral therapy (ART) is essential for controlling HIV-1 replication and boosting immune function. γδ T cells, as a vital component of the innate immune system, are implicated in the antiviral response. However, their immunological profile during acute HIV-1 infection and the early stages of ART remains unclear. This study aimed to delineate the immunological landscape of γδ T cells in individuals with acute HIV-1 infection undergoing early ART. We enrolled 65 participants who initiated ART immediately post-diagnosis and assessed the phenotypes and functions of γδ T cells using flow cytometry. We demonstrated that early ART significantly increased the frequency of Vδ2 T cells, while the Vδ1 T cell frequency remained stable and showed an inverse relationship with CD4+ T cell counts after ART. Early ART normalized the activation and PD-1 expression in Vδ1 and Vδ2 T cells, aligning with healthy controls (HCs) levels. Nevertheless, the proliferation of these cells, particularly within the PD-1+ subset, remains elevated post-ART. We also noted a reduction in perforin secretion in PD-1+ Vδ1 and Vδ2 T cells of people living with HIV (PLWH). Furthermore, Vδ1 T cells were identified as the predominant regulatory T cells, with TGF-β production and co-expression of CD127 and CXCR4, negatively correlated with CD8+ T cell activation. Our study elucidates the dynamic immunological characteristics of γδ T cells in acute HIV-1 infection and early ART, contributing to the understanding of their role in HIV-1 pathogenesis and the potential for γδ T cell-based immunotherapeutic strategies.
Keywords: antiretroviral therapy (ART); early/acute HIV-1 infection; immune activation; regulatory T cells; γδ T cells.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Li, Wang, Wang, Zhang, Lu, Sun, Zhang, Huang, Su, Wu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hellmuth J, Slike BM, Sacdalan C, Best J, Kroon E, Phanuphak N, et al. Very early initiation of antiretroviral therapy during acute hiv infection is associated with normalized levels of immune activation markers in cerebrospinal fluid but not in plasma. J Infect Dis. (2019) 220:1885–91. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiz030 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

