Maternal Diaphragmatic Hernia Correction During Pregnancy
- PMID: 40406557
- PMCID: PMC12094322
- DOI: 10.1097/FM9.0000000000000119
Maternal Diaphragmatic Hernia Correction During Pregnancy
Abstract
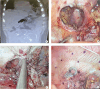
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia consists of a defect in the embryonic development of the diaphragm that allows the passage of the abdominal viscera into the thoracic cavity, its diagnosis during pregnancy is quite rare. We present the case of a 31-year-old woman, with 23 weeks of gestation, who consulted for epigastric pain, nausea, and repetitive emetic episodes, without improvement with the medication provided. Due to the intense abdominal pain, a computed tomography of the abdomen and thorax was performed where the 28 mm defect was found at the left diaphragmatic level with protrusion of the gastric fundus to the thoracic cavity. She was taken to surgical management by laparoscopy with abdominal and thoracic approach, with a successful result and without maternal perinatal complications. Although the integrity of the diaphragmatic suture could be feared in relation to the increase in intraabdominal pressure due to uterine growth, the evolution of our patient and previous reports show that postoperative complications are not frequent. Successful vaginal delivery has even been described in some reports. Diaphragmatic hernias diagnosed during pregnancy are quite rare. We suggest that the optimal management of them during pregnancy is immediate surgical correction in case of persistent symptoms, more studies are needed to establish firm recommendations on the management of this pathology.
Keywords: Bochdalek; Hernias, diaphragmatic, congenital; Pregnancy.
Copyright © 2021 The Chinese Medical Association, published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exacerbation of a maternal hiatus hernia in early pregnancy presenting with symptoms of hyperemesis gravidarum: case report and review of the literature.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2011 Mar;283(3):409-14. doi: 10.1007/s00404-010-1719-3. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2011. PMID: 21042802 Review.
-
A Lady with Severe Abdominal Pain Following a Zumba Dance Session: A Rare Presentation of Bochdalek Hernia.Cureus. 2018 Apr 5;10(4):e2427. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2427. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 29876149 Free PMC article.
-
A tale of two unconventional adult diaphragmatic hernias.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2023 May;105(5):484-488. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2022.0107. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2023. PMID: 36239968 Free PMC article.
-
Rare Right-Sided Posterolateral Diaphragmatic Hernia in an Adult Presenting as an Incarcerated Large Bowel Obstruction: A Case Report.HCA Healthc J Med. 2024 Aug 1;5(4):483-488. doi: 10.36518/2689-0216.1735. eCollection 2024. HCA Healthc J Med. 2024. PMID: 39290486 Free PMC article.
-
Non traumatic right Bochdalek hernia with loss of Domain in adults. Our experience and review of literature.Ann Ital Chir. 2023 Sep 5;12:S2239253X23039877. Ann Ital Chir. 2023. PMID: 37814503 Review.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Hermosa JI Pujadas M Ruiz B, et al. . Hernia diafragmática de Bochdalek en el adulto. Cir Esp 2004;76(3):191–194. 10.1016/S0009-739X(04)78962-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
