Selective Fetal Growth Restriction in Monochorionic Diamniotic Twins: Diagnosis and Management
- PMID: 40406686
- PMCID: PMC12087895
- DOI: 10.1097/FM9.0000000000000171
Selective Fetal Growth Restriction in Monochorionic Diamniotic Twins: Diagnosis and Management
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Selective Fetal Growth Restriction in Monochorionic Diamniotic Twins: Diagnosis and Management: Erratum.Matern Fetal Med. 2023 Jan;5(1):57. doi: 10.1097/FM9.0000000000000176. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Matern Fetal Med. 2023. PMID: 40433234 Free PMC article.
Abstract
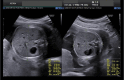
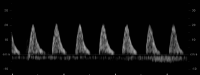
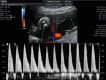
Selective fetal growth restriction (sFGR) is a severe condition that complicates 10% to 15% of all monochorionic diamniotic (MCDA) twin pregnancies. Pregnancies complicated with sFGR are at high risk of intrauterine demise or adverse perinatal outcome for the twins. Three clinical types have been described according to the umbilical artery (UA) Doppler pattern observed in the smaller twin: type I, when the UA Doppler is normal; type II, when there is persistent absent or reversed end-diastolic blood flow in the UA Doppler; and type III, when there is intermittent absent and/or reversed end-diastolic blood flow in the UA Doppler. Clinical evolution and management options mainly depend on the type of sFGR. Type I is usually associated with a good prognosis and is managed conservatively. There is no consensus on the management of types II and III, but in earlier and more severe presentations, fetal interventions such as selective laser photocoagulation of placental anastomoses or selective fetal cord occlusion of the smaller twin may be considered. This review aims to provide updated information about the diagnosis, evaluation, follow-up, and management of sFGR in MCDA twin pregnancies.
Keywords: Birthweight discordance; Fetal therapy; Monochorionic diamniotic twins; Placenta; Selective fetal growth restriction; Twins.
Copyright © 2022 The Chinese Medical Association, published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
