Commissureless acts as a substrate adapter in a conserved Nedd4 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway to promote axon growth across the midline
- PMID: 40407164
- PMCID: PMC12101832
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.92757
Commissureless acts as a substrate adapter in a conserved Nedd4 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway to promote axon growth across the midline
Abstract
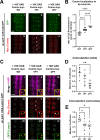
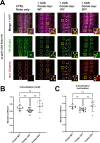
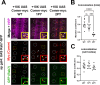
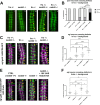
In both vertebrates and invertebrates, commissural neurons prevent premature responsiveness to the midline repellant Slit by downregulating surface levels of its receptor Roundabout1 (Robo1). In Drosophila, Commissureless (Comm) plays a critical role in this process; however, there is conflicting data on the underlying molecular mechanism. Here, we demonstrate that the conserved PY motifs in the cytoplasmic domain of Comm are required allow the ubiquitination and lysosomal degradation of Robo1. Disruption of these motifs prevents Comm from localizing to Lamp1 positive late endosomes and to promote axon growth across the midline in vivo. In addition, we conclusively demonstrate a role for Nedd4 in midline crossing. Genetic analysis shows that nedd4 mutations result in midline crossing defects in the Drosophila embryonic nerve cord, which can be rescued by introduction of exogenous Nedd4. Biochemical evidence shows that Nedd4 incorporates into a three-member complex with Comm and Robo1 in a PY motif-dependent manner. Finally, we present genetic evidence that Nedd4 acts with Comm in the embryonic nerve cord to downregulate Robo1 levels. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that Comm promotes midline crossing in the nerve cord by facilitating Robo1 ubiquitination by Nedd4, ultimately leading to its degradation.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Nedd4; Robo; Slit; axon guidance; commissureless; developmental biology; neuroscience; ubiquitin ligase.
© 2024, Sullivan and Bashaw.
Conflict of interest statement
KS, GB No competing interests declared
Figures





Update of
-
Commissureless acts as a substrate adapter in a conserved Nedd4 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway to promote axon growth across the midline.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 31:2023.10.13.562283. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.13.562283. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 May 23;13:RP92757. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92757. PMID: 37905056 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Commissureless acts as a substrate adapter in a conserved Nedd4 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway to promote axon growth across the midline.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 31:2023.10.13.562283. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.13.562283. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2025 May 23;13:RP92757. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92757. PMID: 37905056 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A Nedd4 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Pathway Inhibits Robo1 Repulsion and Promotes Commissural Axon Guidance across the Midline.J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 5;42(40):7547-7561. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2491-21.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36002265 Free PMC article.
-
Ndfip Proteins Target Robo Receptors for Degradation and Allow Commissural Axons to Cross the Midline in the Developing Spinal Cord.Cell Rep. 2019 Mar 19;26(12):3298-3312.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.080. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30893602 Free PMC article.
-
The Slit-Robo signalling pathway in nervous system development: a comparative perspective from vertebrates and invertebrates.Open Biol. 2025 Jul;15(7):250026. doi: 10.1098/rsob.250026. Epub 2025 Jul 9. Open Biol. 2025. PMID: 40628293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cycling infrastructure for reducing cycling injuries in cyclists.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 10;2015(12):CD010415. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010415.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26661390 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles for E3 ubiquitin ligases in neural development and disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 27;13:1557653. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1557653. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40496139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experience-dependent reconfiguration of receptors at a sensory compartment regulates neuronal plasticity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 13:2025.08.13.670147. doi: 10.1101/2025.08.13.670147. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40855883 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Anitha A, Nakamura K, Yamada K, Suda S, Thanseem I, Tsujii M, Iwayama Y, Hattori E, Toyota T, Miyachi T, Iwata Y, Suzuki K, Matsuzaki H, Kawai M, Sekine Y, Tsuchiya K, Sugihara GI, Ouchi Y, Sugiyama T, Koizumi K, Higashida H, Takei N, Yoshikawa T, Mori N. Genetic analyses of roundabout (ROBO) axon guidance receptors in autism. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics. 2008;147B:1019–1027. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30697. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bakkers J, Camacho-Carvajal M, Nowak M, Kramer C, Danger B, Hammerschmidt M. Destabilization of DeltaNp63alpha by Nedd4-mediated ubiquitination and Ubc9-mediated sumoylation, and its implications on dorsoventral patterning of the zebrafish embryo. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:790–800. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.6.1694. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bosley TM, Salih MAM, Jen JC, Lin DDM, Oystreck D, Abu-Amero KK, MacDonald DB, al Zayed Z, al Dhalaan H, Kansu T, Stigsby B, Baloh RW. Neurologic features of horizontal gaze palsy and progressive scoliosis with mutations in ROBO3. Neurology. 2005;64:1196–1203. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000156349.01765.2B. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

