mKmer: an unbiased K-mer embedding of microbiomic single-microbe RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 40407385
- PMCID: PMC12100620
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbaf227
mKmer: an unbiased K-mer embedding of microbiomic single-microbe RNA sequencing data
Abstract
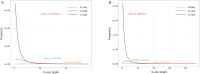
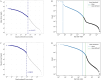
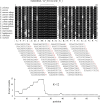
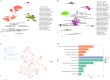
The advanced single-microbe RNA sequencing (smRNA-seq) technique addresses the pressing need to understand the complexity and diversity of microbial communities, as well as the distinct microbial states defined by different gene expression profiles. Current analyses of smRNA-seq data heavily rely on the integrity of reference genomes within the queried microbiota. However, establishing a comprehensive collection of microbial reference genomes or gene sets remains a significant challenge for most real-world microbial ecosystems. Here, we developed an unbiased embedding algorithm utilizing K-mer signatures, named mKmer, which bypasses gene or genome alignment to enable species identification for individual microbes and downstream functional enrichment analysis. By substituting gene features in the canonical cell-by-gene matrix with highly conserved K-mers, we demonstrate that mKmer outperforms gene-based methods in clustering and motif inference tasks using benchmark datasets from crop soil and human gut microbiomes. Our method provides a reference genome-free analytical framework for advancing smRNA-seq studies.
Keywords: K-mer; K-motif; HCK; reference genome-free; smRNA-seq.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High-throughput single-microbe RNA sequencing reveals adaptive state heterogeneity and host-phage activity associations in human gut microbiome.Protein Cell. 2025 Mar 8;16(3):211-226. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae027. Protein Cell. 2025. PMID: 38779805 Free PMC article.
-
16S rRNA sequence embeddings: Meaningful numeric feature representations of nucleotide sequences that are convenient for downstream analyses.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Feb 26;15(2):e1006721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006721. eCollection 2019 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30807567 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of k-mer spectrum applicability for metagenomic dissimilarity analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jan 16;17:38. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0875-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26774270 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the total genome length of a metagenomic sample using k-mers.BMC Genomics. 2019 Apr 4;20(Suppl 2):183. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5467-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30967110 Free PMC article.
-
Supervised application of internal validation measures to benchmark dimensionality reduction methods in scRNA-seq data.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Nov 5;22(6):bbab304. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab304. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34374742 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

