Perceptions, Attitudes, and Concerns on Artificial Intelligence Applications in Patients with Cancer
- PMID: 40407404
- PMCID: PMC12102565
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748251343245
Perceptions, Attitudes, and Concerns on Artificial Intelligence Applications in Patients with Cancer
Abstract
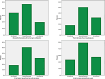
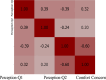
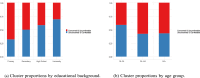
IntroductionThe use of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology has increased rapidly, transforming various healthcare areas such as pathology, radiology, diagnostics, prognosis, genomics, treatment planning, and clinical trials. However, perspectives, comfort levels, and concerns about AI in cancer care remain largely unexplored.Materials and MethodsThis prospective, descriptive cross-sectional survey study was conducted between May 20, 2024 and October 22, 2024, among 363 patients with cancer from two different hospitals affiliated with Ankara University, a tertiary care center in Türkiye. The survey included three distinct sections: (1) Perceptions: Patients' general views on AI's impact in oncology; (2) Attitudes: Comfort level with AI performing medical tasks; (3) Concerns: Specific fears related to AI implementation (eg, diagnostic errors, data privacy, healthcare costs). Survey responses were summarized descriptively, and differences by age, gender, and education were analyzed using chi-square tests.ResultsA majority (50.7%) believed AI would somewhat (32%) or significantly (18.7%) improve healthcare. However, one-third of patients (33.1%) were very uncomfortable with AI diagnosing cancer, with higher discomfort among less-educated participants (P < .005). Top patient concerns included AI making incorrect diagnoses (31.1%), increasing healthcare costs (27.5%), and not keeping data private (19.6%). Patients with higher education levels expressed less discomfort and fewer concerns.ConclusionsPatients' perceptions and attitudes on AI varied significantly based on education, highlighting the need for targeted educational initiatives. While AI holds potential to revolutionize cancer care, addressing concerns about accuracy, security, and transparency is critical to enhance its acceptance and effectiveness in clinical practice.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cancer care; chatbots; comfort levels; healthcare concerns; machine learning and deep learning systems; natural language processing; patient perspectives.
Plain language summary
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an important tool in cancer care, assisting in diagnosis, treatment planning, and clinical decision-making. However, not all patients feel comfortable with AI being used in their medical care. This study surveyed 363 cancer patients to understand their perspectives on AI in oncology. Findings revealed that while many patients believe AI can improve healthcare, others have concerns about diagnostic accuracy, data privacy, and the economic impact of AI-driven medical decisions. Patients with higher education levels showed greater acceptance of AI. To ensure that AI is effectively integrated into oncology, policymakers and healthcare professionals must address these concerns, enhance patient education, and establish ethical guidelines for AI applications in medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices among Healthcare Professionals toward Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare.J Assoc Physicians India. 2025 Apr;73(4):e6-e12. doi: 10.59556/japi.73.0909. J Assoc Physicians India. 2025. PMID: 40200614
-
Patient Perspectives on AI for Mental Health Care: Cross-Sectional Survey Study.JMIR Ment Health. 2024 Sep 18;11:e58462. doi: 10.2196/58462. JMIR Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 39293056 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the integration of artificial intelligence in the medical education curriculum: a mixed-methods study exploring the perspectives of medical students and faculty in Pakistan.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Feb 20;25(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06552-2. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 39979912 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Medicine: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jun;24(6):e70241. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70241. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40501296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) in restorative dentistry: current trends and future prospects.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05989-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40251567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Han SS, Kim YJ, Moon IJ, et al. Evaluation of artificial intelligence–assisted diagnosis of skin neoplasms: a single-center, paralleled, unmasked, randomized controlled trial. J Invest Dermatol. 2022;142(9):2353-2362.e2352. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

