Development and Characterization of a Ten-Plex Assay to Measure Klebsiella pneumoniae Antigen-Specific IgG in Human Sera
- PMID: 40407479
- PMCID: PMC12101422
- DOI: 10.3390/mps8030052
Development and Characterization of a Ten-Plex Assay to Measure Klebsiella pneumoniae Antigen-Specific IgG in Human Sera
Abstract
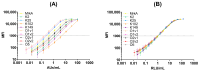
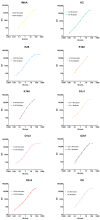
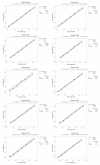
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a leading cause of nosocomial infections, neonatal sepsis, and childhood mortality worldwide. A drastic rise in antibiotic-resistant isolates poses an urgent threat to humanity, and the World Health Organization (WHO) has classified this as a critical-priority antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) pathogen. Recent advancements in developing vaccines against Klebsiella pneumoniae have highlighted the lack of standardized assays to evaluate immunogenicity, complicating comparison among different vaccines under development and the establishment of a serological threshold of risk reduction (SToRR). Here, we describe the development of a ten-plex multiplex assay to measure IgG against capsular polysaccharides (K2, K25, K102, K149), O antigens (O1v1, O1v2, O2v1, O2v2 and O5), and a conserved protein (MrkA). A standard curve was established by pooling human sera from naturally exposed subjects and then calibrated in terms of Relative Luminex Units/mL. The assay was fully characterized in terms of specificity, precision, linearity, and repeatability. This immunoassay demonstrates performance suitable for future clinical trials, as well as to perform sero-epidemiological studies to gain insights into naturally occurring immunity, potentially contributing to the establishment of a serological threshold of risk reduction against Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Keywords: IgG quantification; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Luminex; immunogenicity; multiplex assay; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was performed with funds from the Gates Foundation and with internal funding from GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Gates Foundation. GSK Vaccines Institute for Global Health Srl is an affiliate of GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. L.R., G.F.B., L.M., F.N., R.A., M.M., D.O., M.T., S.R., M.I., C.G., F.M., M.C. and O.R. are employees of the GSK group of companies. S.A.M. received funding from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Minervax, Merk, and funds from Gates Foundation all fully unrelated to the study described in this project.
Figures

References
-
- Sands K., Carvalho M.J., Portal E., Thomson K., Dyer C., Akpulu C., Andrews R., Ferreira A., Gillespie D., Hender T., et al. Characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Gram-negative bacteria that cause neonatal sepsis in seven low- and middle-income countries. Nat. Microbiol. 2021;6:512–523. doi: 10.1038/s41564-021-00870-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance. 2024. [(accessed on 14 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461. - PubMed
-
- Kumar C.K., Sands K., Walsh T.R., O’Brien S., Sharland M., Lewnard J.A., Hu H., Srikantiah P., Laxminarayan R. Global, regional, and national estimates of the impact of a maternal Klebsiella pneumoniae vaccine: A Bayesian modeling analysis. PLoS Med. 2023;20:e1004239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004239. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

