Severe Aplastic Anemia Complicated with Fatal Invasive Fungal Infections in a Young Patient Harboring Perforin Gene Polymorphisms
- PMID: 40407635
- PMCID: PMC12101316
- DOI: 10.3390/hematolrep17030025
Severe Aplastic Anemia Complicated with Fatal Invasive Fungal Infections in a Young Patient Harboring Perforin Gene Polymorphisms
Abstract
Background: Severe aplastic anemia (SAA) is an uncommon life-threatening disorder characterized by hypocellular bone marrow and pancytopenia. It is typically associated with immune-mediated mechanisms, requiring immunosuppressive therapy (IST) or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Infections, especially invasive fungal infections such as mucormycosis and aspergillosis, constitute principal causes of morbidity and mortality in patients with SAA. Genetic predispositions, including perforin (PRF1) polymorphisms, may further complicate disease outcomes by impairing immune function.
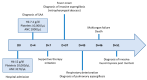
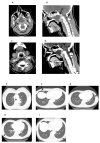
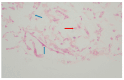
Case report: We describe a case of a 36-year-old female patient diagnosed with SAA, for whom IST was considered, due to the unavailability of a matched sibling donor for HSCT. The patient presented with a feverish condition and deep neck space abscesses were revealed by imaging, caused by invasive aspergillosis. To prioritize infection control, IST was postponed and antifungal therapy with abscess drainage was initiated. However, aspergillosis progressed, despite aggressive and prompt treatment, and ultimately resulted in sepsis, multiorgan failure, and death. In addition, mucormycosis was confirmed post-mortem. Two heterozygous PRF1 polymorphisms (c.272C>T and c.900C>T), were identified by genetic testing, which may have contributed to immune dysregulation and fungal dissemination.
Conclusions: The complex interplay between managing SAA and addressing invasive fungal infections, which remain a leading cause of mortality in immunocompromised patients, is highlighted in this case. The latter emphasizes the importance of prompt diagnosis and targeted treatment to alleviate infection-related complications while maintaining care continuity for the hematologic disorder. The detection of PRF1 polymorphisms raises questions about their implication in immune regulation and disease trajectory, emphasizing the need for further research in this field.
Keywords: aspergillosis; immunosuppressive therapy; mucormycosis; perforin gene mutation; severe aplastic anemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kulasekararaj A., Cavenagh J., Dokal I., Foukaneli T., Gandhi S., Garg M., Griffin M., Hillmen P., Ireland R., Killick S., et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of adult aplastic anaemia: A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br. J. Haematol. 2024;204:784–804. doi: 10.1111/bjh.19236. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

