A Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis and COVID-19-Related Pneumonia in a Pembrolizumab-Treated Patient
- PMID: 40407655
- PMCID: PMC12101223
- DOI: 10.3390/idr17030053
A Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis and COVID-19-Related Pneumonia in a Pembrolizumab-Treated Patient
Abstract
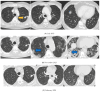
Pembrolizumab is used as a first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Pneumonitis and interstitial lung disease are among the most common immune-related adverse events. The impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections on patients with cancer treated with chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) is not fully known. Blocking immune checkpoints may conversely augment dysfunctional T-cell responses in severe patients and, in turn, mediate immunopathology. Here, we present a case of SARS-CoV-2 infection complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and a fibrotic-like pattern in a patient treated with pembrolizumab for lung cancer. The patient showed a dramatic clinical and radiological response after steroid therapy. Further research is needed to better understand the long-term implications of pembrolizumab therapy in patients recovering from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and to develop evidence-based guidelines for managing these complex cases. Patients undergoing oncologic immunotherapy might benefit from early high-dose steroid treatment in cases of viral infections, such as SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: fibrotic-like pattern; pembrolizumab; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pillai R.N., Behera M., Owonikoko T.K., Kamphorst A.O., Pakkala S., Belani C.P., Khuri F.R., Ahmed R., Ramalingam S.S. Comparison of the toxicity profile of PD-1 versus PD-L1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic analysis of the literature. Cancer. 2018;124:271–277. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ono K., Ono H., Toi Y., Sugisaka J., Aso M., Saito R., Kawana S., Aiba T., Odaka T., Matsuda S., et al. Association of immune-related pneumonitis with clinical benefit of anti-programmed cell death-1 monotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2021;10:4796–4804. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

