Temperature-modulated separation of therapeutic cells, viral vectors, and exosomes using functional polymers
- PMID: 40408001
- PMCID: PMC12307572
- DOI: 10.1007/s44211-025-00785-x
Temperature-modulated separation of therapeutic cells, viral vectors, and exosomes using functional polymers
Abstract
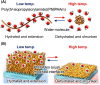
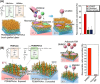
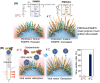
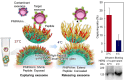
In recent decades, advanced therapeutic modalities such as therapeutic cells, viral vectors, and extracellular vesicles (exosomes), have emerged as effective therapies for intractable diseases. These therapeutic modalities produced through bioprocesses must be purified from contaminants. Effective separation methods are essential for optimizing therapeutic modalities. This review highlights innovative temperature-modulated separation methods enabled by the thermoresponsive polymer poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAm). The design of PNIPAAm-modified interfaces plays a pivotal role in ensuring precise and efficient separation. We summarize the recent advancements in the application of temperature-modulated separation methods for cells, viral vectors, and exosomes, with a focus on the design of PNIPAAm interfaces.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Polymer brush; Regenerative medicine; Temperature-responsive chromatography; Thermoresponsive interface; Thermoresponsive polymer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: There are no competing interests to declare.
Figures


References
-
- M. Heskins, J.E. Guillet, Solution properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Macromol. Sci. A 2, 1441–1455 (1968). 10.1080/10601326808051910
-
- E.S. Gil, S.M. Hudson, Stimuli-reponsive polymers and their bioconjugates. Prog. Polym. Sci. 29, 1173–1222 (2004). 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.08.003
-
- A. Halperin, M. Kröger, F.M. Winnik, Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) phase diagrams: fifty years of research. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 15342–15367 (2015). 10.1002/anie.201506663 - PubMed
-
- K. Nagase, T. Onuma, M. Yamato, N. Takeda, T. Okano, Enhanced wettability changes by synergistic effect of micro/nanoimprinted substrates and grafted thermoresponsive polymer brushes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 36, 1965–1970 (2015). 10.1002/marc.201500393 - PubMed
-
- K. Nagase, J. Matsuda, A. Takeuchi, Y. Ikemoto, Hydration and dehydration behaviors of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted silica beads. Surf. Interf. 40, 103058 (2023). 10.1016/j.surfin.2023.103058
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

