Updated Overall Survival and Long-Term Safety With Ripretinib Versus Sunitinib in Patients With GI Stromal Tumor: Final Overall Survival Analysis From INTRIGUE
- PMID: 40408605
- PMCID: PMC12225728
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-24-02818
Updated Overall Survival and Long-Term Safety With Ripretinib Versus Sunitinib in Patients With GI Stromal Tumor: Final Overall Survival Analysis From INTRIGUE
Abstract
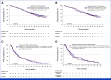
In the INTRIGUE phase III trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03673501), adult patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor previously treated with imatinib were randomly assigned 1:1 to ripretinib 150 mg once daily or sunitinib 50 mg once daily (4 weeks on/2 weeks off). In the primary analysis, overall survival (OS) was immature. In this study, we report the final planned analysis of OS (key secondary end point), progression-free survival (PFS) on third-line therapy (second PFS; prespecified exploratory end point), and long-term safety. Final OS analysis was prespecified to occur with approximately 200 and ≥145 events in the overall and KIT exon 11 intention-to-treat (ITT) populations, respectively. As of March 15, 2023, there were 211 and 151 OS events in the overall ITT and KIT exon 11 ITT populations, respectively. Median OS was similar between second-line ripretinib and sunitinib in both populations (overall, 35.5 v 31.5 months; KIT exon 11, 35.5 v 32.8 months). Median second PFS (on third-line therapy) for the overall ITT population was similar between the ripretinib and sunitinib arms (7.7 v 7.4 months). Safety was consistent with the primary analysis. OS from this analysis was similar between arms, and second PFS suggests that receiving ripretinib did not adversely affect the PFS of third-line therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Demetri GD, et al. : Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol 21:4342-4349, 2003 - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Version 1.2025. 2025. https://www.nccn.org
-
- Nemunaitis J, Bauer S, Blay JY, et al. : INTRIGUE: Phase III study of ripretinib versus sunitinib in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor after imatinib. Future Oncol 16:4251-4264, 2020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

