Cutaneous Lupus Features Specialized Stromal Niches and Altered Retroelement Expression
- PMID: 40409678
- PMCID: PMC12354343
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2025.04.033
Cutaneous Lupus Features Specialized Stromal Niches and Altered Retroelement Expression
Abstract
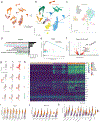
Cutaneous lupus is an inflammatory skin disease causing highly morbid inflamed skin and hair loss. To investigate the pathophysiology of cutaneous lupus, we performed single-cell RNA and spatial sequencing of lesional and nonlesional cutaneous lupus skin compared with that of healthy controls. Pathway enrichment analyses of lesional keratinocytes revealed elevated responses to IFN-I, IFN-II, TNF, and apoptotic signaling. Detailed clustering demonstrated unique fibroblasts specific to lupus skin with likely roles in inflammatory cell recruitment and fibrosis. We also evaluated the association of retroelement expression with IFN-I in the skin. We observed increased retroelement expression that correlated with IFN-stimulated genes across multiple cell types. Moreover, we saw elevated expression of genes involved in RIG-I and cGAS-STING pathways, which transduce elevated nucleic acid signals. Treatment of active cutaneous lupus with anifrolumab reduced RIG-I and cGAS-STING pathways in addition to the most abundant retroelement family, L2b. Our studies better define IFN-I IFN-mediated immunopathology in cutaneous lupus and identify an association between retroelement expression and IFN signatures in cutaneous lupus.
Keywords: Anifrolumab; Cutaneous lupus; Fibroblasts; IFN; Retroelements.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
Disclosures: A.I. co-founded RIGImmune, Xanadu Bio and PanV; and is a member of the Board of Directors of Roche Holding Ltd and Genentech. J.R.G has received research funding support from Bristol Meyers Squibb. The authors declare that these relationships did not influence the design, execution, interpretation, or reporting of the research presented in this manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Hile GA, Kahlenberg JM. Immunopathogenesis of skin injury in systemic lupus erythematosus. 2020; Available from:www.co-rheumatology.com - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

