Oral ENPP1 inhibitor designed using generative AI as next generation STING modulator for solid tumors
- PMID: 40410143
- PMCID: PMC12102218
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59874-0
Oral ENPP1 inhibitor designed using generative AI as next generation STING modulator for solid tumors
Abstract
Despite the STING-type-I interferon pathway playing a key role in effective anti-tumor immunity, the therapeutic benefit of direct STING agonists appears limited. In this study, we use several artificial intelligence techniques and patient-based multi-omics data to show that Ectonucleotide Pyrophosphatase/Phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1), which hydrolyzes STING-activating cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), is a safer and more effective STING-modulating target than direct STING agonism in multiple solid tumors. We then leverage our generative chemistry artificial intelligence-based drug design platform to facilitate the design of ISM5939, an orally bioavailable ENPP1-selective inhibitor capable of stabilizing extracellular cGAMP and activating bystander antigen-presenting cells without inducing either toxic inflammatory cytokine release or tumor-infiltrating T-cell death. In murine syngeneic models across cancer types, ISM5939 synergizes with targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis and chemotherapy in suppressing tumor growth with good tolerance. Our findings provide evidence supporting ENPP1 as an innate immune checkpoint across solid tumors and reports an AI design-aided ENPP1 inhibitor, ISM5939, as a cutting-edge STING modulator for cancer therapy, paving a path for immunotherapy advancements.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The Authors declare the following competing interests: All listed authors are affiliated with Insilico Medicine, a global clinical-stage commercial generative AI company with several hundred patents and patent applications and commercially available software. Insilico Medicine is a company developing an AI-based end-to-end integrated pipeline for drug discovery and development that is engaged in drug-discovery programs for aging, fibrosis and oncology. C.P., H.C., H.Y., X.C., M.Z., L.Q., Z.N., W.Z., S.C., L.W., X.L., D.G., F.W.P., F.R., and A.Z. are affiliated with Insilico Medicine or were affiliated with Insilico Medicine when the studies were performed. The remaining authors declare no competing interest. No other conflicts are reported.
Figures
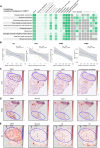
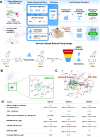
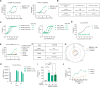
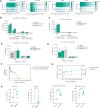


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

