Enhancing the potency of in vivo lentiviral vector mediated gene therapy to hepatocytes
- PMID: 40410162
- PMCID: PMC12102377
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60073-0
Enhancing the potency of in vivo lentiviral vector mediated gene therapy to hepatocytes
Abstract
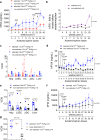
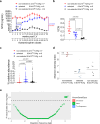
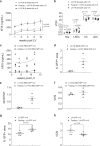
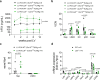
In vivo gene therapy to the liver using lentiviral vectors (LV) may represent a one-and-done therapeutic approach for monogenic diseases. Increasing LV gene therapy potency is crucial for reducing the effective doses, thus alleviating dose-dependent toxicities and facilitating manufacturing. LV-mediated liver transduction may be enhanced by positively selecting LV-transduced hepatocytes after treatment (a posteriori) or by augmenting the initial fraction of LV-targeted hepatocytes (a priori). We show here that the a posteriori enhancement increased transgene output without expansion of hepatocytes bearing LV genomic integrations near cancer genes, in mouse models of hemophilia, an inherited coagulation disorder. Furthermore, we enhanced hepatocyte transduction a priori in mice by transiently inhibiting antiviral pathways and/or through a fasting regimen. The most promising transduction-enhancer combination synergized with phagocytosis-shielded LV, resulting in a remarkable 40-fold increase in transgene output. Overall, our work highlights the potential of minimally invasive, cost-effective treatments capable of improving the potency of in vivo LV gene therapy to hepatocytes, in order to expand its applicability and ease clinical translation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: C.C. and A.C. are inventors on patent applications submitted by Fondazione Telethon, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, on LV technology related to the work presented in this manuscript. Fondazione Telethon and San Raffaele Scientific Institute, through SR-Tiget, have established a research collaboration on liver-directed LV gene therapy of hemophilia with GeneSpire. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zabaleta, N., Unzu, C., Weber, N. D. & Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza, G. Gene therapy for liver diseases - progress and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.20, 288–305 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Mahlangu, J. et al. Two-year outcomes of valoctocogene roxaparvovec therapy for hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med388, 694–705 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Pipe, S. W. et al. Gene therapy with etranacogene dezaparvovec for hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med388, 706–718 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

