Superior Capacitive Energy Storage of BaTiO3-Based Polymorphic Relaxor Ferroelectrics Engineered by Mesoscopically Chemical Homogeneity
- PMID: 40411412
- PMCID: PMC12279175
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202502916
Superior Capacitive Energy Storage of BaTiO3-Based Polymorphic Relaxor Ferroelectrics Engineered by Mesoscopically Chemical Homogeneity
Abstract
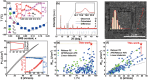
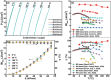
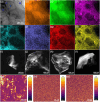
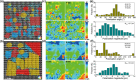
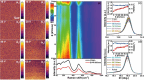
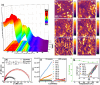
Relaxor ferroelectrics exhibit giant potentials in capacitive energy storage, however, the scales of polar nanoregions determine the critical field values where the polarization saturation occurs. In this work, a mesoscopic structure engineered ergodic relaxor state is realized by adjusting submicron-grain scaled chemical homogenity, exhibiting polymorphic polar nanoregions of various scales in different grains. This produces a relatively continuous polarization switching with increasing the applied electric field from diverse grains, thus resulting in a linear-like polarization response feature. As a result, both a giant energy density (Wrec) ≈15.4 J cm-3 and a field-insensitive ultrahigh efficiency (η) ≈93.2% are simultaneously achieved at 78 kV mm-1 in (Ba, Ca)(Ti, Zr)O3-(Bi0.5Na0.5)SnO3 lead-free ceramics. Moreover, both the mesoscopic structure heterogeneity and complex high internal stresses in ultrafine grains decrease the temperature sensitivity of the nanodomain structural features. Together with the suppressed high-temperature defect motion from high ceramic density and submicron grain size, a record-high temperature stability with Wrec = 10.4±5% J cm-3 and η = 96±3% is obtained at 65 kV mm-1 and 0-250 °C, demonstrating great application potential of the studied ceramic in high-temperature energy storage capacitors. The proposed strategy in this work greatly expands the design mentality for next-generation high-performance energy-storage dielectrics.
Keywords: energy storage capacitors; ex‐/in situ multiscale structure evolution; mesoscopically chemical homogeneity; polymorphic polar nanodomains; relaxor ferroelectrics.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-NaNbO3-Bi(Mg1/2Zr1/2)O3 Lead-Free Relaxor Antiferroelectric Ceramics Featuring Ultrahigh Temperature-Insensitive Energy-Storage Performance.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Jul 16;17(28):40690-40698. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c06895. Epub 2025 Jul 2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40600421
-
Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-Based Relaxor Ferroelectrics with Highly Polarizable Concentrated Nanodomains for High Capacitive Energy Storage under Moderate Electric Fields.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Sep 3;17(35):49421-49432. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c08878. Epub 2025 Aug 20. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40833826
-
Innovative Design of BNKT-xSLZT Ceramics: Maximizing the Polarization Difference for Enhanced Energy Storage.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Apr 24;16(16):20485-20496. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c01348. Epub 2024 Apr 11. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38605498
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Zhang M., Lan S., Yang B. B., Pan H., Liu Y. Q., Zhang Q. H., Qi J. L., Chen D., Su H., Yi D., Yang Y. Y., Wei R., Cai H. D., Han H. J., Gu L., Nan C. W., Lin Y. H., Science 2024, 384, 185. - PubMed
-
- Cheema S. S., Shanker N., Hsu S. L., Schaadt J., Ellis N. M., Cook M., Rastogi R., Pilawa‐Podgurski R. C. N., Ciston J., Mohamed M., Salahuddin S., Nature 2024, 629, 803. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L. Y., Jing R. Y., Huang Y. Y., Yang Y. L., Li Y., Tang M. Y., Cao S. Y., Chen Z. B., Gao F., Du Y. X., Zhou S. Y., Zhao J. W., Liu S. Y., Wang D. W., Zhang S. J., Jin L., Ultra Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2406219. - PubMed
-
- Gao Y. F., Qiao W. J., Lou X. J., Song Z. Z., Zhu X. P., He L. Q., Yang B., Hu Y. H., Shao J. Y., Wang D. Y., Chen Z. B., Zhang S. J., Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 2310559. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2022YFB3807403/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 52302131/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2308085QE140/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province
- 2022AH010058/innovation team project in universities and colleges
- 2023AH050953/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Provincial Education Department
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
