Health-related quality-of-life profile and clinical outcomes in first-line advanced renal cell carcinoma: a modeling analysis based on the CheckMate 9ER study
- PMID: 40412006
- PMCID: PMC12152543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.105115
Health-related quality-of-life profile and clinical outcomes in first-line advanced renal cell carcinoma: a modeling analysis based on the CheckMate 9ER study
Abstract
Background: For patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma, maintaining quality of life during treatment is a priority. The phase III CheckMate 9ER study demonstrated improved efficacy and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) outcomes with first-line cabozantinib plus nivolumab (CaboNivo) versus sunitinib (Sun) and underscored the need to improve understanding of the relationship between clinical efficacy and the patient treatment experience. In this work, we investigated the relationship between changes in HRQoL and clinical outcomes, as well as identifying symptom-based patient profiles that could predict disease course and clinical outcomes.
Materials and methods: This post hoc analysis of CheckMate 9ER used the patient-reported outcomes 19-item Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Kidney Symptom Index (FKSI-19) to evaluate HRQoL. Cox proportional modeling was used to investigate the association between early changes in FKSI-19 scores and clinical outcomes, while latent class analysis (LCA) was used to identify symptom-based patient profiles.
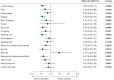
Results: The nature of patient-reported symptoms was similar at baseline and 13 weeks for CaboNivo and Sun, but symptom frequency varied between arms. Early worsening of bone pain [hazard ratio (HR) 1.45, P = 0.010] and sleep quality (HR 1.45, P = 0.007) were associated with increased risk of mortality. The LCA identified three distinct subgroups of patients by symptom burden and risk profile. Patients in the limited symptoms class at week 13 were more likely to have received CaboNivo (limited: 63.4%; moderate-to-severe: 45.9%; severe: 38.5%), had a longer duration of treatment (>122 weeks: 37.2% versus 14.7% versus 17.9%), and were generally less likely to experience disease progression (61.6% versus 55.1% versus 76.9%) than other symptom classes.
Conclusions: This post hoc analysis identified an association between efficacy and HRQoL based on data from CheckMate 9ER. These results highlight the necessity of balancing treatment choice, tolerability, and HRQoL to optimize treatment outcomes and support shared decision-making.
Keywords: CheckMate 9ER; advanced renal cell carcinoma; cabozantinib; health-related quality of life; nivolumab; patient-reported outcomes.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Axitinib, cabozantinib, everolimus, nivolumab, sunitinib and best supportive care in previously treated renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2018 Jan;22(6):1-278. doi: 10.3310/hta22060. Health Technol Assess. 2018. PMID: 29393024 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-reported outcomes with first-line nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated in CheckMate 9ER: an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2022 Feb;23(2):292-303. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00693-8. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Lancet Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35032437 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab for untreated advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Aug;28(49):1-190. doi: 10.3310/TRRM4238. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39252678 Free PMC article.
-
First-line therapy for adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 4;5(5):CD013798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37146227 Free PMC article.
-
A network meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of first-line and second-line therapies for the management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021 Feb;46(1):35-49. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13282. Epub 2020 Oct 28. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021. PMID: 33112003
References
-
- European Medicines Agency Cabometyx® (cabozantinib) EU Summary of Product Characteristics. 2023. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/cabometyx-epa... Available at.
-
- US Food and Drug Administration Cabometyx® (cabozantinib) Prescribing Information. 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2023/208692s016lbl.pdf Available at.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

